Security researchers have published a detailed proof-of-concept demonstrating how attackers can exploit a critical vulnerability in Cisco IOS XE Wireless Controller Software, enabling unauthorized file uploads and potential remote code execution on enterprise wireless infrastructure.
The vulnerability, affecting version 17.12.03 and earlier, stems from a hard-coded JSON Web Token (JWT) that bypasses authentication mechanisms, creating significant security risks for organizations deploying Cisco’s widely-used wireless management platform.
The security flaw was identified through comparative analysis of vulnerable and patched Cisco IOS XE firmware images, specifically comparing C9800-CL-universalk9.17.12.03.iso and C9800-CL-universalk9.17.12.04.iso.
Researchers discovered that the vulnerability lies within the application’s JWT verification mechanism, where the system falls back to a predictable “notfound” string when the expected secret key file is missing from /tmp/nginx_jwt_key.
The affected system utilizes OpenResty, a web platform integrating Lua with Nginx, to handle authentication and file upload operations.
Critical components identified include ewlc_jwt_verify.lua and ewlc_jwt_upload_files.lua scripts located in /var/scripts/lua/features/, which process JWT tokens and manage file uploads respectively.
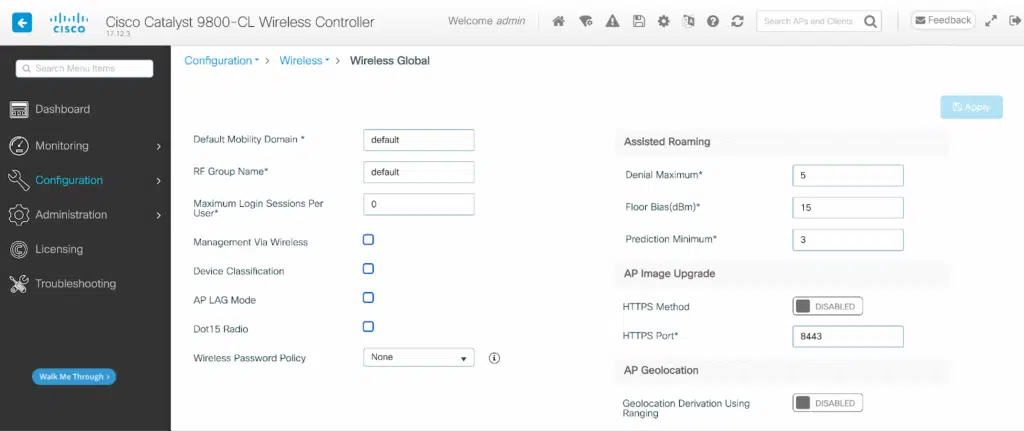
The vulnerability becomes exploitable when the Out-of-Band AP Image Download feature is enabled, exposing upload endpoints on port 8443.
Proof of Concept
The attack vector leverages two main upload endpoints: /aparchive/upload and /ap_spec_rec/upload/, both of which utilize the vulnerable JWT verification process.
When the system cannot locate the proper JWT secret key, it defaults to the hard-coded “notfound” value, allowing attackers to generate valid authentication tokens.
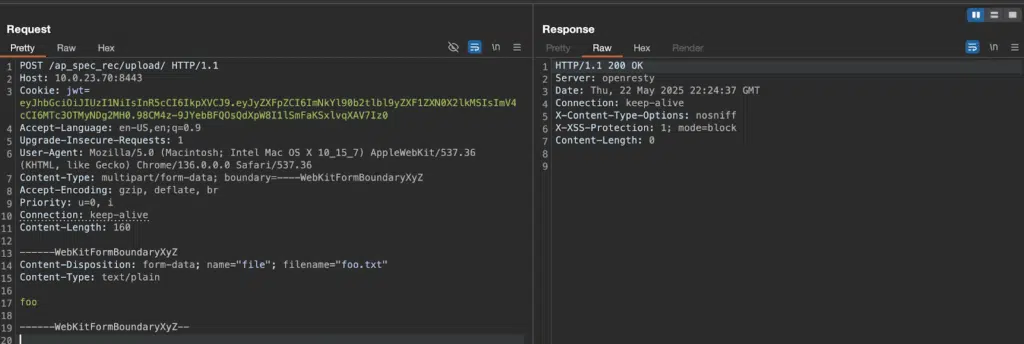
Researchers demonstrated that attackers can craft malicious JWTs using the predictable secret and exploit path traversal vulnerabilities in the file upload mechanism.
The upload functionality fails to properly sanitize filenames, enabling attackers to use directory traversal sequences like ../ to write files outside the intended upload directory.
By targeting the /usr/binos/openresty/nginx/html directory, attackers can place malicious files directly in the web server’s document root.
The proof-of-concept further revealed that remote code execution is achievable by exploiting internal process management services that monitor file changes using inotifywait.
Attackers can overwrite configuration files and trigger service reloads, ultimately gaining administrative access to the affected systems.
Mitigations
The vulnerability poses severe risks to enterprise wireless infrastructure, as Cisco IOS XE Wireless LAN Controllers manage large-scale wireless networks across campus and branch environments.
Successful exploitation grants attackers unauthorized file upload capabilities and potential complete system compromise through remote code execution.
Cisco has addressed the vulnerability in version 17.12.04 and strongly recommends immediate upgrades.
For organizations unable to upgrade immediately, Cisco suggests disabling the Out-of-Band AP Image Download feature as a temporary mitigation measure.
This workaround forces the system to use CAPWAP methods for AP image updates, which do not expose the vulnerable endpoints.
Notably, researchers observed that port 8443 remained accessible by default on fresh WLC installations, even without explicitly enabling the AP Image Upgrade feature, suggesting broader exposure than initially anticipated.
Organizations should prioritize patching efforts and conduct thorough security assessments of their wireless infrastructure to identify potential compromise indicators.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates.