Misconfigured containers in Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) environments can expose sensitive AWS credentials through two primary attack vectors: packet sniffing and API spoofing.
Trend Micro research reveals that containers with excessive privileges, particularly those configured with hostNetwork: true or elevated Linux capabilities CAP_NET_ADMIN—can intercept or manipulate credential exchange processes.
This vulnerability stems from the EKS Pod Identity agent’s unencrypted HTTP API endpoint at 169.254.170.23:80, which transmits credentials in plaintext.
AWS maintains that this falls under customer responsibility within their shared security model.
Packet Sniffing Exploit
Containers with hostNetwork: true Enabled can monitor node traffic and intercept unencrypted credentials from the EKS Pod Identity API.
Using standard tools like tcpdumpAttackers capture AWS credentials transmitted to 169.254.170.23:80.
Since these credentials aren’t bound to specific hosts, malicious actors can reuse them for privilege escalation across AWS environments.
The attack requires no advanced permissions beyond network visibility, making it accessible even to low-privilege adversaries.
API Spoofing Technique
Containers with CAP_NET_ADMIN capabilities can hijack the credential service by manipulating network interfaces.
Attackers disable the eks-pod-identity-agent HTTP daemon, then deploy a malicious HTTP server on the same IP (169.254.170.23:80).
This spoofed server intercepts Kubernetes service account tokens from the Authorization header, which are then exchanged for valid AWS credentials via the AssumeRoleForPodIdentity API1.
Trend Micro’s Python PoC using pyroute2 demonstrates how attackers can automate this process.
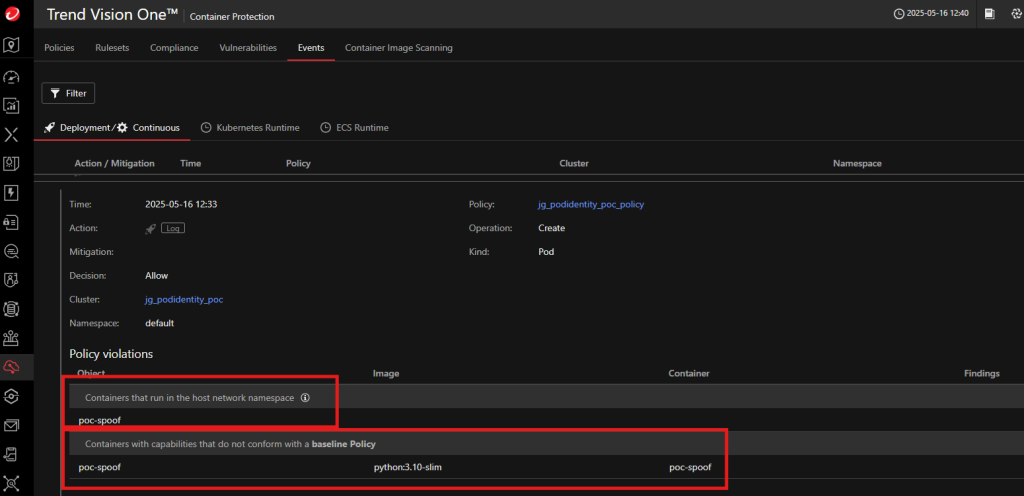
Mitigation Strategies
Implement least-privilege principles through:
- Configuration hardening:
- Disable
hostNetwork: trueunless required - Restrict Linux capabilities using
securityContextdrop lists - Apply pod security policies blocking privileged containers
- Disable
- Runtime monitoring:
- Trend Vision One policies flagging “containers in host network namespace” or “non-baseline capabilities”
- Amazon GuardDuty detects anomalous privileged container deployments
- Credential binding:
AWS recommends scoping IAM roles to minimize the blast radius if credentials are compromised.
These exposures highlight the critical need for continuous container privilege auditing alongside network encryption enhancements in Kubernetes credential services.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant updates