Unrelenting since its debut in 2011, SmokeLoader has transformed from a rudimentary downloader into a formidable, modular framework for deploying secondary malware such as ransomware, trojans, and information-stealing plugins.
Although Operation Endgame in May 2024 a joint effort between global law enforcement and Zscaler ThreatLabz successfully eradicated many instances, SmokeLoader resurfaced in early 2025 with two new variants: version 2025 alpha and version 2025.
These releases not only remedy prior performance flaws but also incorporate advanced evasion techniques to frustrate static and behavior-based detection.
Evolution of Stager and Mutex Safeguards
SmokeLoader’s infection sequence begins with a compact stager whose primary role is to verify the execution environment and then inject the main module into explorer.exe. Earlier builds suffered from uncontrolled reinjection every ten minutes triggered by a scheduled task leading to system slowdowns.
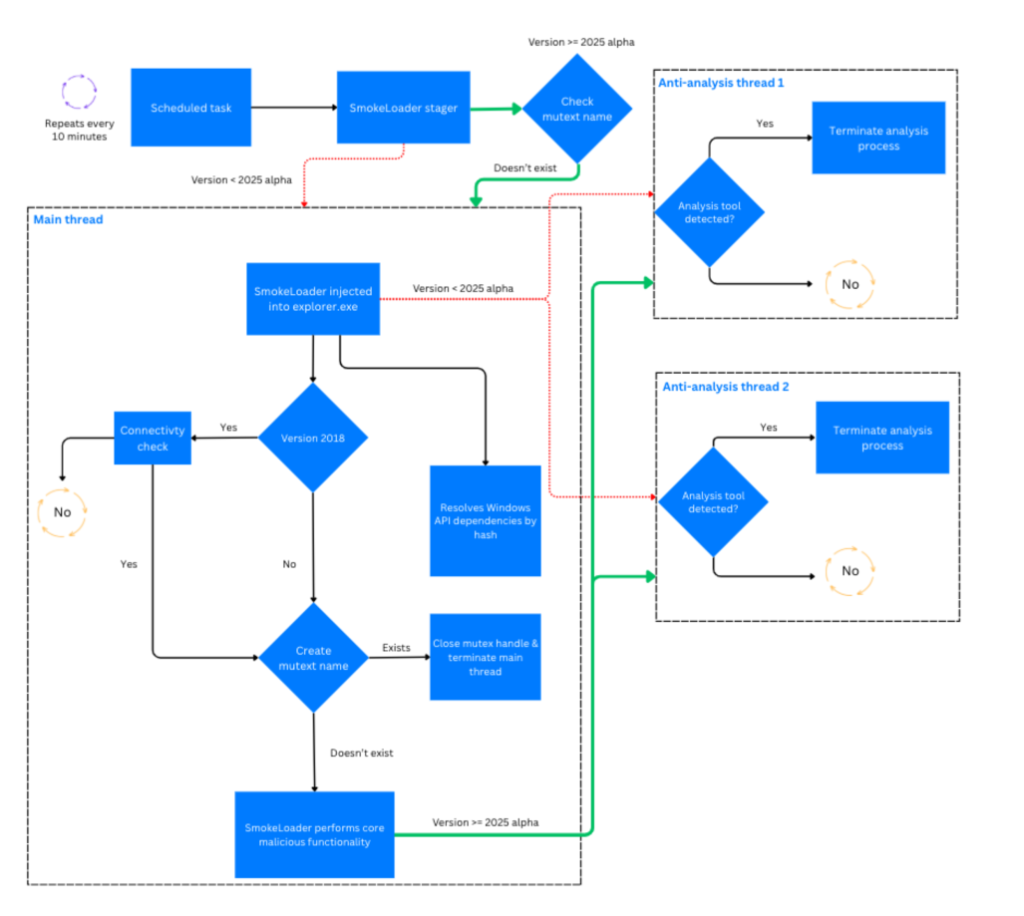
Version 2025 alpha introduces a robust mutex check in the stager, preventing duplicate injections and redundant thread creation. This mutex, formerly a uniform 40-character uppercase hexadecimal string, now emerges as a pseudo-random lowercase alphabetic sequence.
The sequence length and content derive from a linear congruential generator seeded with the first four bytes of the bot ID.
Once in memory, the main module establishes persistence through a scheduled task named “MicrosoftEdgeUpdateTaskMachine” followed by the initial 16 characters of the bot ID.
It then proceeds to beacon to its command-and-control (C2) servers, manage plugins, and enforce a second mutex check, terminating if another instance is detected.
Both the stager and the main module now employ XOR-based obfuscation routines with per-sample keys for constants and strings, complicating signature-based detection.
Network communications retain a text-based, RC4-encrypted POST protocol in version 2025 alpha, mirroring the venerable 2022 format. Version 2025 upgrades this exchange by embedding a two-byte version marker (0x7E9) and a CRC32 checksum at byte offset two, covering the payload beyond offset six.
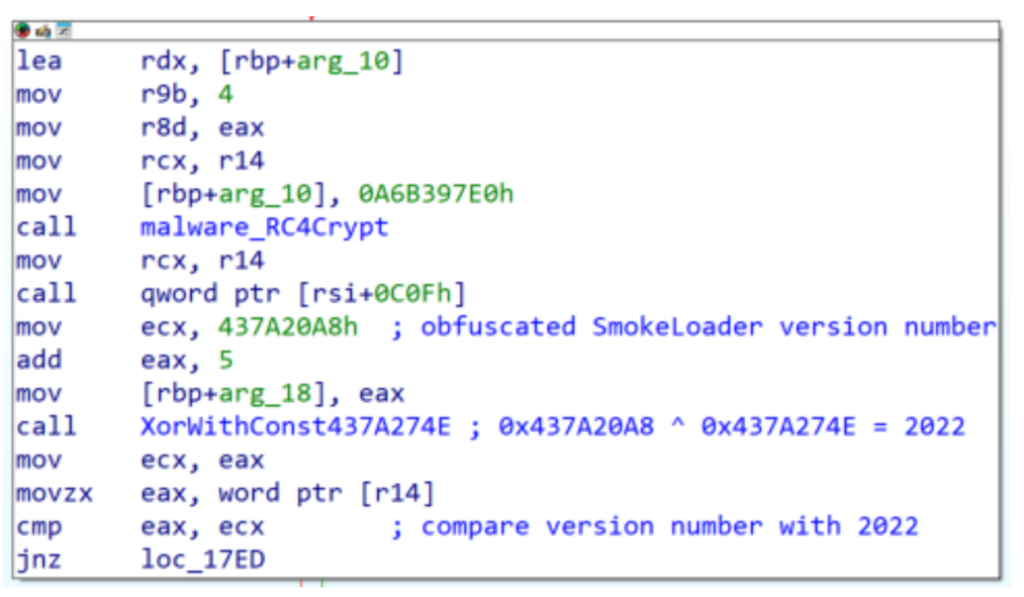
Additionally, the initial response length field is now XOR’d with the RC4 key, thwarting simple protocol analysis.
SmokeLoader’s true potency lies in its plugin architecture. Initial panels leaked in 2012 supported commands like getgrab, getproxy, and getspoof, fetching modules for credential harvesting, SOCKS proxying, and hosts-file tampering.
Subsequent iterations merged individual stealers into a consolidated “plugins” module capable of exfiltrating browser credentials, FTP and mail passwords, and keystrokes. Optional modules for distributed denial-of-service attacks and cryptocurrency mining further diversify its malicious toolbox.
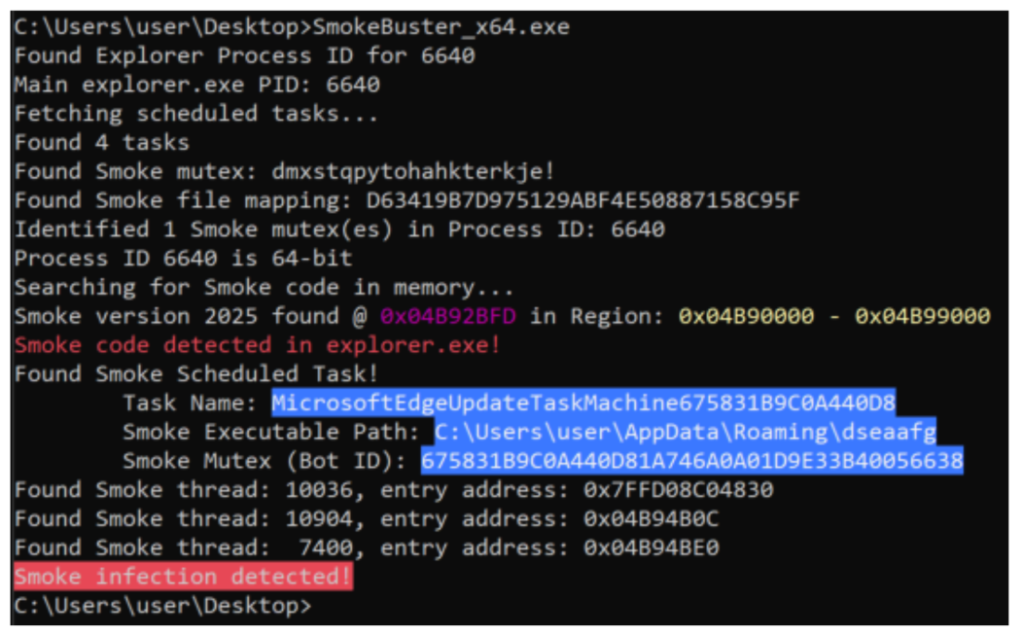
To counter this adaptable threat, Zscaler ThreatLabz released SmokeBuster, an open-source sanitization utility updated to recognize and eradicate the latest 2025 alpha and 2025 variants.
By scanning for active mutex patterns, scheduled tasks, and C2 beacons, SmokeBuster can neutralize infections and uninstall rogue modules.
SmokeLoader’s persistence and continual refinements underscore its status as an enduring menace. While backward compatibility has driven the adoption of version 2025 alpha, the stealthier protocol tweaks and obfuscation enhancements in version 2025 are poised to become the next standard for this resilient loader.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates