Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a sophisticated malware campaign that exploits Windows shortcut (.LNK) files distributed through Discord to deploy a multi-functional Remote Access Trojan (RAT).
The attack demonstrates advanced evasion techniques by abusing legitimate Windows binaries and bypassing multiple security mechanisms.
The malicious LNK file, disguised as “cyber security.lnk,” presents users with a fake job offer PDF while silently executing PowerShell commands in the background.
When clicked, the shortcut opens a decoy document titled “Cyber Security.pdf” to distract victims while deploying its payload through a carefully orchestrated infection chain.
Living-off-the-Land Binary Abuse
The malware’s most notable feature is its abuse of odbcconf.exe, a legitimate Windows command-line tool typically used for configuring ODBC drivers. The attack uses this Living-off-the-Land Binary (LOLBin) to execute a malicious DLL named Moq.dll without triggering security alerts.
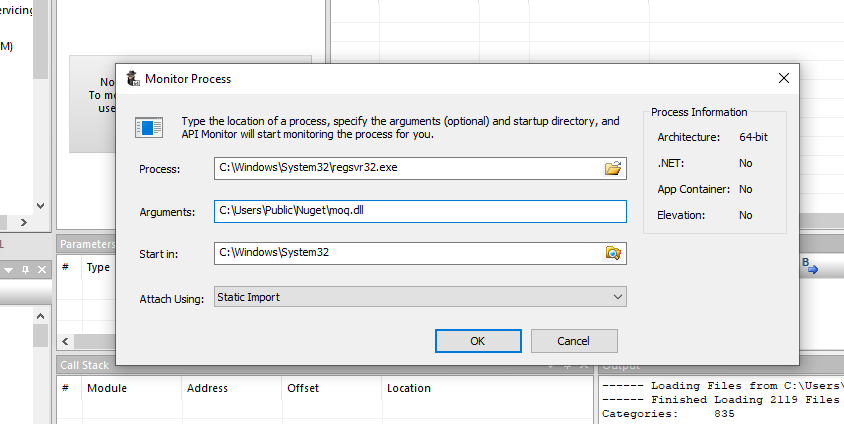
The PowerShell script extracts an embedded ZIP file containing the malicious payload and executes it using the command: odbcconf.exe /a {regsvr "C:\Users\Public\Nuget\moq.dll"}.
This technique effectively bypasses traditional security tools by leveraging a trusted Windows binary for malicious purposes. The malware creates a hidden “NuGet” folder in the Public directory to store its components, including supporting DLLs like Dapper.dll and Newtonsoft.dll.
Advanced Evasion Techniques
Moq.dll implements multiple sophisticated evasion mechanisms to avoid detection. The malware patches the AmsiScanBuffer function by overwriting its first six bytes with assembly code that forces the Anti-Malware Scan Interface (AMSI) always to fail, effectively neutralizing Windows’ built-in malware scanning capabilities.
Similarly, the RAT disables Windows Event Tracing (ETW) by patching the EtwEventWrite function in ntdll.dll, preventing security solutions from monitoring its activities through event logs. These patches use identical byte sequences that redirect both functions to return failure codes immediately.
The malware achieves persistence by modifying the Windows registry key HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Shell, ensuring it executes alongside explorer.exe during every user login.
It establishes communication with its command and control server at hotchickenfly.info and generates unique machine identifiers for tracking infected systems.
The RAT’s capabilities include capturing screenshots, collecting system information about installed antivirus software, and exfiltrating data through Dropbox’s API using hardcoded tokens. The malware encrypts its communications and commands using AES encryption to avoid network detection.
Security researchers from K7 Labs identified this threat, which was first observed in Israel. The attack highlights the growing trend of malware authors leveraging legitimate Windows utilities to evade detection while deploying sophisticated RATs capable of comprehensive system compromise.
Organizations should implement application whitelisting, monitor LOLBin usage, and deploy endpoint detection solutions capable of identifying behavioral anomalies to defend against such advanced threats.
IOC’s
| Hash | Detection Name |
| 7391C3D895246DBD5D26BF70F1D8CBAD | Trojan ( 0001140e1) |
| 2956ec73ec77757271e612b81ca122c4 | Trojan ( 0001140e1) |
| 5a1d0e023f696d094d6f7b25f459391f | Trojan ( 0001140e1) |
| 92fc7724688108d3ad841f3d2ce19dc7 | Trojan (0001140e1 ) |
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates