A sophisticated new malware family dubbed LAMEHUG has emerged as the first known threat to weaponize artificial intelligence for dynamic attack execution, marking a significant evolution in cybercriminal tactics.
First identified by CERT-UA in July 2025, this Python-based malware leverages large language models hosted on Hugging Face to generate real-time Windows commands for reconnaissance and data exfiltration.
Step-by-step illustration of the spear phishing email attack cycle from attacker to data exfiltration
Unlike traditional malware that relies on pre-programmed command sequences, LAMEHUG integrates the Qwen 2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct model to dynamically craft system commands based on the target environment.
The malware queries the AI model through Hugging Face APIs, receiving tailored instructions for gathering system information, harvesting credentials, and collecting files that adapt to each compromised host.
The threat actors distribute LAMEHUG through spear-phishing campaigns disguised as legitimate AI applications. Filenames such as “AI_generator_uncensored_Canvas_PRO_v0.9.exe” and “AI_image_generator_v0.95.exe” masquerade as popular AI tools to deceive victims.
Upon execution, the malware launches a separate thread running the malicious LLM_QUERY_EX() function while maintaining the facade of a functional image generator.
Advanced Evasion Through AI-Generated Commands
The malware’s most concerning capability is its ability to generate real-time commands. LAMEHUG constructs prompts that instruct the AI model to produce Windows shell commands for specific reconnaissance tasks.
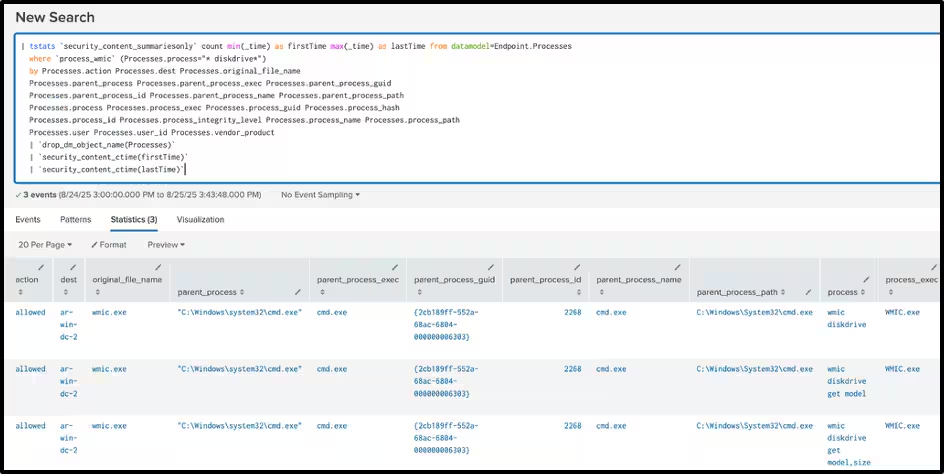
These AI-generated commands utilize utilities such as systeminfo, wmic, whoami, and dsquery to collect comprehensive system intelligence, while xcopy.exe facilitates targeted document collection from multiple directory paths.
Analysis by the Splunk Threat Research Team revealed that LAMEHUG systematically harvests sensitive files, consolidating documents into C:\ProgramData\info for exfiltration.
The malware targets various file types, including .doc, .docx, .pdf, and database files, demonstrating sophisticated data collection capabilities driven by AI-generated instructions.
For command and control communications, LAMEHUG employs multiple protocols, including SSH and HTTPS.
One variant utilizes hardcoded SSH credentials to transmit stolen data to remote servers. At the same time, another encodes LLM queries in Base64 and exfiltrates data via HTTPS POST requests to domains such as stayathomeclasses[.]com.
The Splunk research team developed comprehensive detection capabilities through 14 analytic rules targeting LAMEHUG’s behavior patterns.
Key detection focuses include monitoring WMIC commands for system discovery (CPU, disk, memory, network), tracking file collection via copy utilities, and identifying DNS queries to Hugging Face infrastructure – particularly “router.huggingface.co” from processes like python.exe and cmd.exe.
This AI-powered approach represents a paradigm shift in malware development, enabling threats that adapt their behavior in real-time rather than following static command sequences.
As cybercriminals increasingly weaponize artificial intelligence, organizations must enhance detection capabilities to identify these dynamic, AI-driven attack methodologies that challenge traditional signature-based security approaches.
IOC
| SHA256 Hashes | Description |
|---|---|
| 384e8f3d300205546fb8c9b9224011b3b3cb71adc994180ff55e1e6416f65715 | LAMEHUG |
| 766c356d6a4b00078a0293460c5967764fcd788da8c1cd1df708695f3a15b777 | LAMEHUG |
| bdb33bbb4ea11884b15f67e5c974136e6294aa87459cdc276ac2eea85b1deaa3 | LAMEHUG |
| d6af1c9f5ce407e53ec73c8e7187ed804fb4f80cf8dbd6722fc69e15e135db2e | LAMEHUG |
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates