BlueNoroff, a North Korean threat actor also tracked as Sapphire Sleet, APT38, and Alluring Pisces, has significantly evolved its attack methodology targeting high-value individuals in the blockchain and Web3 sectors.
Security researchers have identified two sophisticated campaigns, GhostCall and GhostHire, that demonstrate the group’s increased operational sophistication and utilization of artificial intelligence to refine targeting and execution capabilities.
The campaigns specifically target cryptocurrency developers, venture capitalists, and executive-level personnel within Web3 organizations as part of the SnatchCrypto operation.
GhostCall: Deceptive Video Meetings and Credential Harvesting
The GhostCall campaign represents a significant shift in BlueNoroff’s social engineering approach. Rather than using deepfake technology, threat actors leverage recordings of actual victims obtained through prior compromises to create a seemingly legitimate meeting experience.
Initial contact occurs via Telegram, where attackers impersonate venture capitalists and entrepreneurs, sometimes using compromised accounts of legitimate founders to schedule meetings through fake Zoom or Microsoft Teams interfaces.
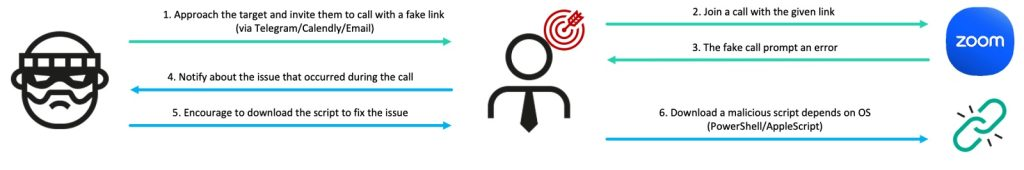
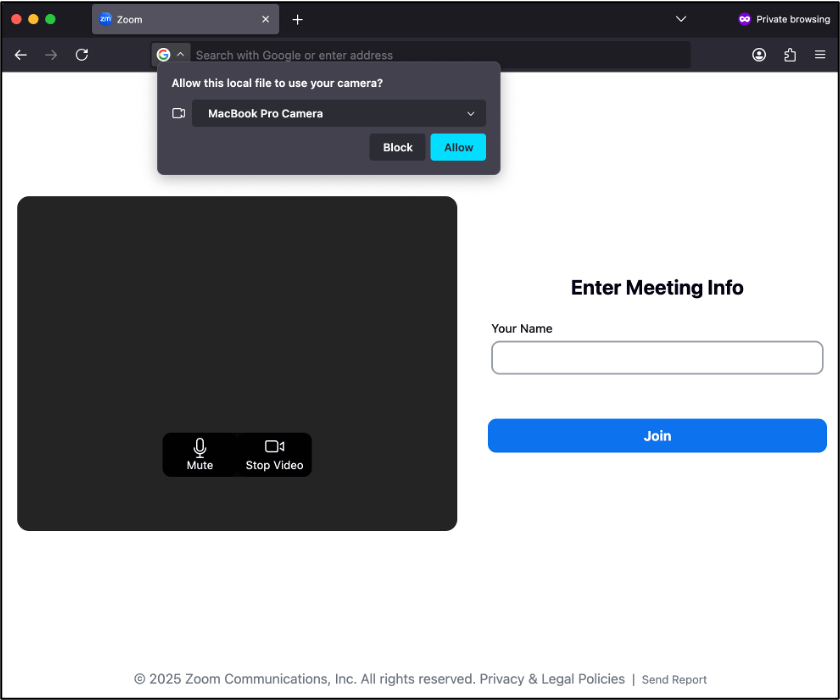
Once victims access the phishing site, they encounter a page meticulously designed to replicate legitimate videoconferencing platforms. The JavaScript logic records video feeds and uploads them to the attacker’s infrastructure every second.
When the victim joins the fake meeting, they witness three participants whose video feeds are actually authentic recordings stolen from previous victims. After three to five seconds, an error message appears prompting users to download a fake Zoom SDK update.
On macOS, clicking the update link downloads a malicious AppleScript file disguised as “Zoom SDK Update.scpt.” This script contains approximately 10,000 blank lines that obscure its malicious code, then fetches another AppleScript downloader using curl.
For macOS versions 11 (Monterey) and later, the infection chain deploys fake Zoom or Microsoft Teams applications that harvest system passwords while displaying authentic Apple password prompts.
The malware validates credentials against macOS Open Directory before exfiltration, filtering out incorrect entries.
A critical technical component involves bypassing macOS Transparency, Consent, and Control (TCC) protections.
The malware renames the com. apple.TCC directory and performs offline database edits, removing existing access entries and inserting new permissions for AppleEvents automation and file system access to actor-controlled paths.
This enables subsequent malware stages to operate with elevated privileges without user prompts.
Multi-Stage Infection Infrastructure
Kaspersky researchers identified seven distinct multi-component infection chains deployed via centralized file-hosting servers.
These modular chains utilize various programming languages, including Nim, Go, Python, C++, Rust, and Swift, representing a strategic shift from purely Rust-based malware observed in earlier operations.
The infection chains incorporate sophisticated components, including CosmicDoor (a Nim-based backdoor communicating via WSS protocol), RealTimeTroy (a Go-based backdoor), and DownTroy (an AppleScript-based downloader).
The modular stealer suite harvests cryptocurrency wallets, Keychain data, cloud credentials, API keys, and browser-stored credentials. Beaconing infrastructure tracks victim interactions through HTTP GET requests, allowing attackers to assess targeting success.
The technical sophistication demonstrates BlueNoroff’s continued investment in infrastructure, malware development, and social engineering capabilities to compromise high-value targets within the blockchain industry.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates