A critical vulnerability identified as CVE‑2025‑11749 with a CVSS score of 9.8 has been discovered in the AI Engine WordPress plugin, which is active on more than 100,000 websites.
The flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to retrieve an exposed bearer token from the MCP REST API, granting them full administrative privileges on affected sites.
This issue was reported by Emiliano Versini through the Wordfence Bug Bounty Program on October 4, 2025, and patched by developer Jordy Meow in version 3.1.4 released on October 19, 2025.
Sensitive Information Exposure Leading to Privilege Escalation (CVE‑2025‑11749)
The vulnerability resides in the plugin’s Model Context Protocol (MCP) integration, which enables AI systems such as ChatGPT or Claude to interact with WordPress, performing actions like content editing and site management.
Versions up to and including 3.1.3 failed to include the parameter “show_in_index => false” during REST route registration, leaving “No‑Auth URL” endpoints publicly visible in the /wp-json/ REST API index.
When enabled, this feature exposes the MCP bearer token in the URL path, allowing any unauthenticated user to access it. Once obtained, an attacker could authenticate to the MCP endpoint and execute privileged commands such as wp_update_user, elevating their role to Administrator.
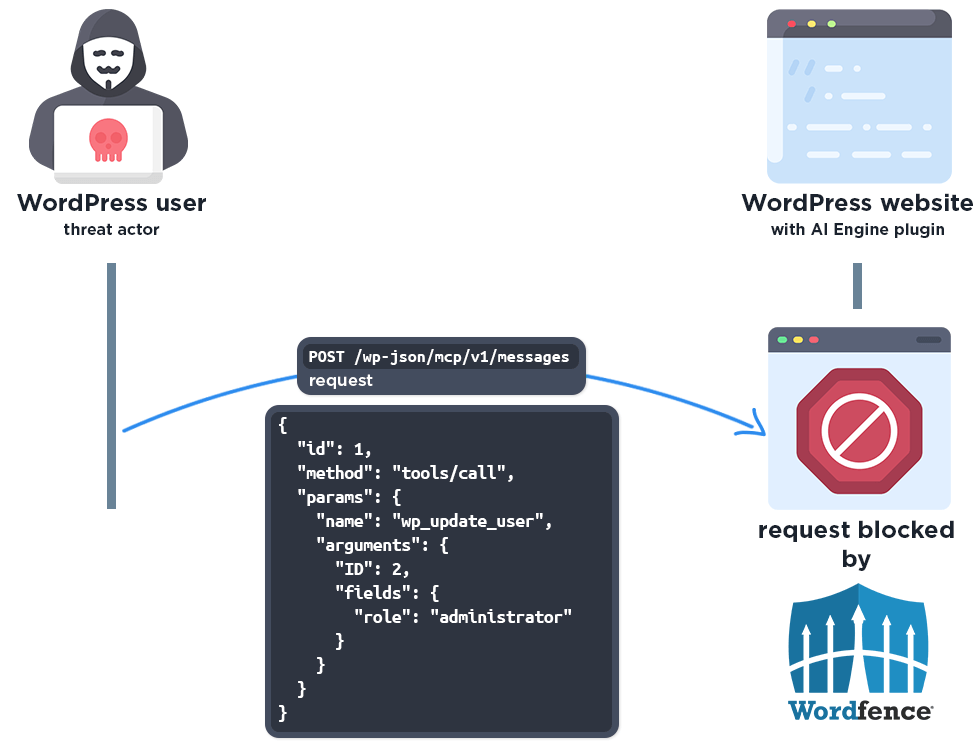
This complete privilege escalation would permit attackers to install backdoors or malicious plugins, alter site content, and compromise the integrity of the entire WordPress installation.
Wordfence Premium, Care, and Response users received an immediate firewall rule on October 15, 2025, to block exploit attempts. Free Wordfence users will receive the same protection on November 14, 2025.
Affected site owners should update to version 3.1.4 or newer and immediately rotate the MCP bearer token to prevent unauthorized access, since any exposed token remains compromised even after patching.
The vulnerability only critically impacts those who had manually enabled the “No‑Auth URL” setting, which is disabled by default.
| CVE ID | CVSS 3.1 | Affected Versions | Patched Version | Researcher | Bounty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE‑2025‑11749 | 9.8 (Critical) | ≤ 3.1.3 | 3.1.4 | Emiliano Versini | $2,145 |
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates