A critical Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) vulnerability has been discovered in OpenAI’s ChatGPT Custom GPTs feature, allowing attackers to access sensitive cloud credentials and internal metadata services.
Security researcher SirLeeroyJenkins identified the flaw while exploring the platform’s “Actions” feature, which enables custom GPTs to interact with external APIs.
The vulnerability stemmed from insufficient validation of user-provided URLs in the Custom GPTs Actions section.
Attackers could craft malicious API configurations that point to internal services, tricking ChatGPT’s servers into making unauthorized requests to Azure’s metadata service at 169.254.169.254.
This internal metadata service contains critical cloud credentials and configuration data that should only be accessible to authorized cloud resources.
The researcher bypassed initial HTTPS-only restrictions using HTTP 302 redirects, forcing the server to follow redirection chains to unencrypted internal endpoints.
By manipulating authentication headers through the API key configuration, specifically setting a custom header named “Metadata” with the value “True,” the attacker successfully authenticated to Azure’s metadata service.
This enabled the extraction of valid Azure Management API access tokens, granting direct access to OpenAI’s cloud infrastructure.
The exploitation chain demonstrated how seemingly innocent features can create critical security gaps when cloud security principles aren’t properly implemented.
The vulnerability illustrates why SSRF attacks have become increasingly dangerous as major technology companies adopt the cloud.
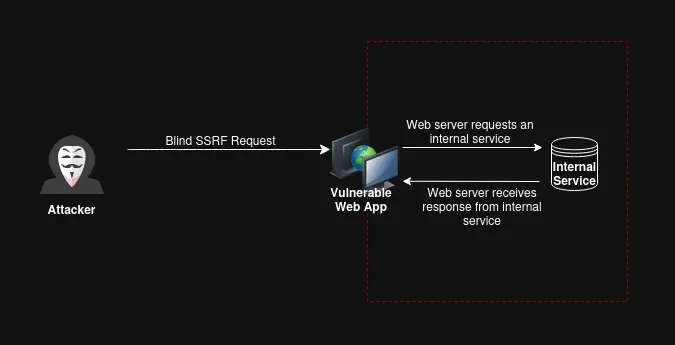
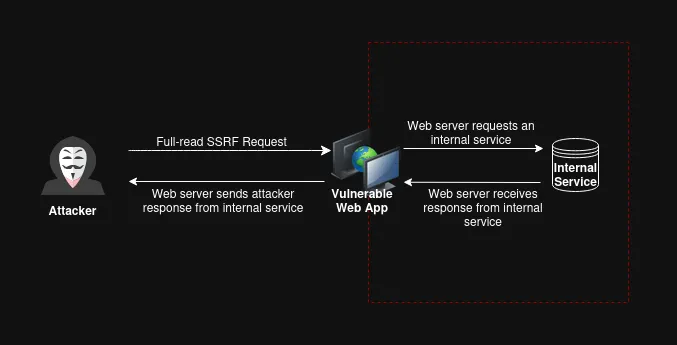
The 2021 OWASP Top 10 list recognized SSRF as a critical vulnerability class due to its potential to escalate privileges and compromise the entire infrastructure.
OpenAI immediately patched the vulnerability upon disclosure through their Bugcrowd bug bounty program, rating it as high severity.
While this particular SSRF didn’t enable remote code execution like previous discoveries affecting major firms, it demonstrated the persistent threat posed by inadequate input validation in AI platform features.
The incident underscores the importance of validating and restricting all outbound requests from application servers, particularly in cloud environments where metadata services represent a critical security perimeter.
Security teams should review their custom GPT configurations and implement strict URL allowlists for API integrations, while cloud providers must continue hardening metadata service protections.
| CVE ID | Vendor | Product | Vulnerability Type | Severity | Status | Disclosed | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A (Unreported CVE) | OpenAI | ChatGPT Custom GPTs | Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) | High | Patched | November 2024 | Unauthorized access to Azure metadata service, cloud credential extraction |
| CVE-2021-44228 | Apache | Log4j | Remote Code Execution via JNDI | Critical | Patched | December 2021 | Complete system compromise via malicious LDAP/RMI injection |
| CVE-2021-3129 | Laravel | Framework | Remote Code Execution via File Upload | Critical | Patched | January 2021 | Arbitrary code execution through deserialization vulnerability |
| CVE-2019-9193 | PostgreSQL | Database | Remote Code Execution via COPY TO | High | Patched | November 2019 | Arbitrary file write and potential RCE through database commands |
Implement strict URL validation and allowlisting for all external API calls. Use network segmentation to isolate metadata services from application servers. Enforce HTTPS enforcement at the application level with certificate pinning.
Deploy cloud-native security controls to restrict IMDS access through authentication headers and network policies.
Conduct regular security audits of all third-party integration features, particularly those accepting user-controlled parameters for network requests.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates