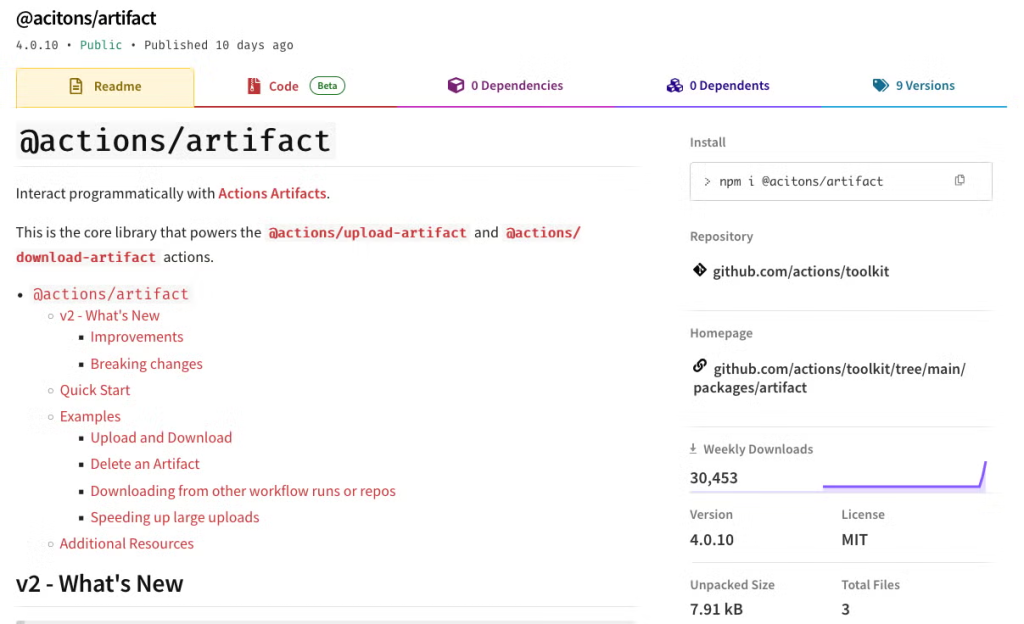
A malicious npm package, “@acitons/artifact,” was uncovered by Veracode Threat Research on Friday, November 7th, leveraging typosquatting to masquerade as the trusted “@actions/artifact” package, which has more than 206,000 downloads to date.
This campaign strategically targeted GitHub-owned repositories, aiming to exfiltrate sensitive build environment tokens and potentially publish malicious content posing as legitimate GitHub artifacts.
Malicious Package Exploits GitHub Actions CI/CD
The threat actor behind “@acitons/artifact” released six versions containing a post-install hook designed to fetch and execute a stealthy binary named “ci_test_harness” from a remote source.
The binary was so subtle and obfuscated that, as of the initial analysis, it evaded detection by all major antivirus engines on VirusTotal.
Within the package.json for version 4.0.13, the post-install script executed a curl command that downloaded the malicious binary, altered its permissions, and ran it within the CI/CD pipeline environment.
Upon manual review, researchers identified an embedded expiry mechanism that would block execution after November 6, 2025, suggesting a time-limited campaign window and advanced attacker planning.
Technical Analysis: Targeted Attack on GitHub
The “ci_test_harness” binary was compiled with the SHC (Shell Script Compiler), enabling stronger obfuscation and making static analysis more difficult. The malware included runtime checks for GitHub environment variables set in GitHub Actions.
Its payload is activated only if the repository owner matches “github”, making the attack highly focused on GitHub’s own repositories.
Once running, the script extracted and executed a node package containing a heavily obfuscated “verify.js” file. This script acquired an AES key from a third-party DNS resolution service and encrypted gathered data, including GitHub tokens.
The exfiltration targeted a concealed endpoint hosted as a GitHub App on the developer platform, using HTTPS.
Impact, Remediation, and Supply Chain Security
The malicious versions were quickly removed from npm, reportedly by the threat actor or by GitHub’s intervention, leaving only older, benign versions publicly accessible.
VirusTotal’s behavioral analysis now confirms suspicious activity tied to the original payload, though initial scans missed it completely.
This targeted software supply chain attack serves as a case study for OWASP’s newly prioritized “A03:2025-Software Supply Chain Failures” in its Top 10 for 2025, underscoring industry-wide concerns about the integrity of the package ecosystem.
Organizations using Veracode’s Package Firewall were automatically protected, highlighting the critical need for proactive defense mechanisms in CI/CD environments.
The incident illustrates both the sophistication of modern software supply chain threats and the necessity of rigorous monitoring and dependency verification within DevOps pipelines, especially in environments as widely adopted as GitHub Actions.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates