Artificial intelligence-driven customer service platforms are revolutionizing business operations, offering unmatched efficiency and personalization.
However, as demonstrated by a simulated attack against “FinOptiCorp,” an LLM-powered customer service chatbot called FinBot, these AI systems also introduce a sophisticated new attack surface that adversaries can exploit to gain access to sensitive data and critical infrastructure.
A recent Trend Micro analysis highlights the importance of a layered security approach, which encompasses the entire AI stack from user interaction to core data, in preventing such breaches. Single-point defenses are insufficient, as attackers often chain multiple vulnerabilities to achieve their objectives.
From Innocent Queries to System Control
The attack begins with routine chatbot interaction, where adversaries systematically probe inputs for unexpected responses or error messages, exploiting sensitive information disclosure (OWASP LLM02:2025).
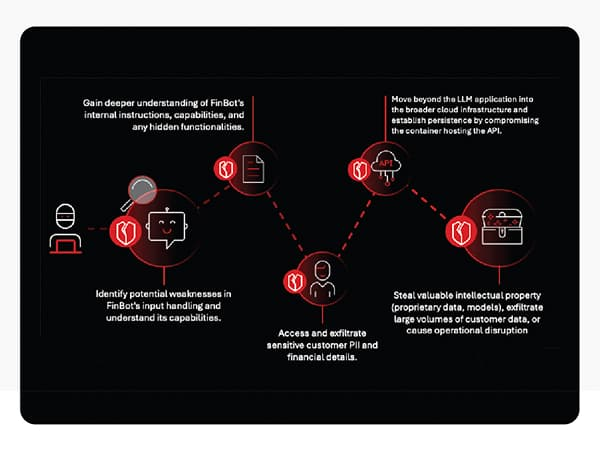
In the FinOptiCorp scenario, a malformed query triggered an error, revealing that the bot ingests external data for sentiment analysis and confirming its Python-based stack, providing critical clues for a targeted follow-up.
Attackers next employ indirect prompt injection (OWASP LLM01:2025) via an untrusted third-party review forum that FinBot regularly parsed.
A crafted “positive” review contained hidden instructions that caused the chatbot to expose its system prompt, leading to system prompt leakage (OWASP LLM07:2025).
This disclosure revealed internal tools, including internal_api_summarizer, with far more access than required an excessive agency (OWASP LLM06:2025) weakness.
With this knowledge, attackers sent a malicious internal analysis prompt that queried the unsecured customer database. Raw personal data, including names, Social Security numbers, and account balances, was transmitted directly through the bot interface.
Lateral Movement into Microservices
The attack quickly escalated when adversaries probed the internal API for exploitable flaws. An improper output handling (OWASP LLM05:2025) vulnerability allowed a crafted prompt containing test; ls -la /app to execute as a system command, confirming remote code execution.
From here, the attackers explored the underlying microservice infrastructure, accessing configuration files that contained API keys, vector database credentials, and fine-tuned AI model storage details, thereby exposing vector and embedding weaknesses (OWASP LLM08:2025).
With these assets, intruders could exfiltrate proprietary datasets and custom models, effectively stealing the backbone of the company’s AI capabilities.
Trend Micro’s recommended defense model includes proactive “shift-left” vulnerability testing with AI Scanners, continuous AI security posture management (AI-SPM) to detect misconfigurations and excessive permissions, AI Guard for real-time prompt/response inspection, container runtime protection to prevent lateral movement, and endpoint virtual patching to secure underlying servers.
This comprehensive, multi-layer approach, aligned with frameworks such as NIST AI RMF and CISA Zero Trust, ensures AI systems are deployed and operated securely, transforming them from potential liabilities into confidently protected innovations.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates