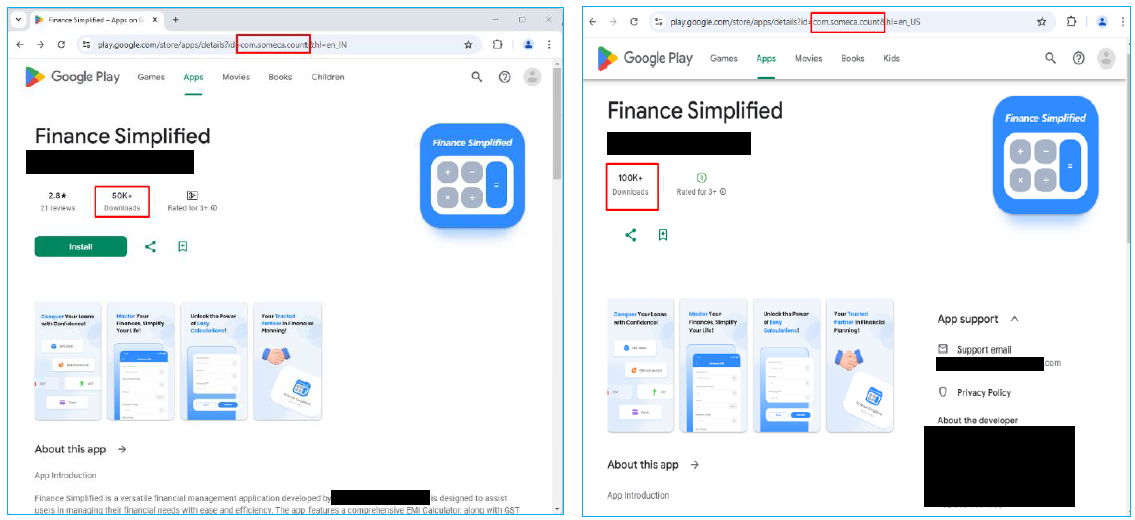
A recent cybersecurity investigation has uncovered a malicious Android app on the Google Play Store, known as “Finance Simplified,” which has been exploiting Indian users by stealing sensitive data and engaging in financial cybercrime.
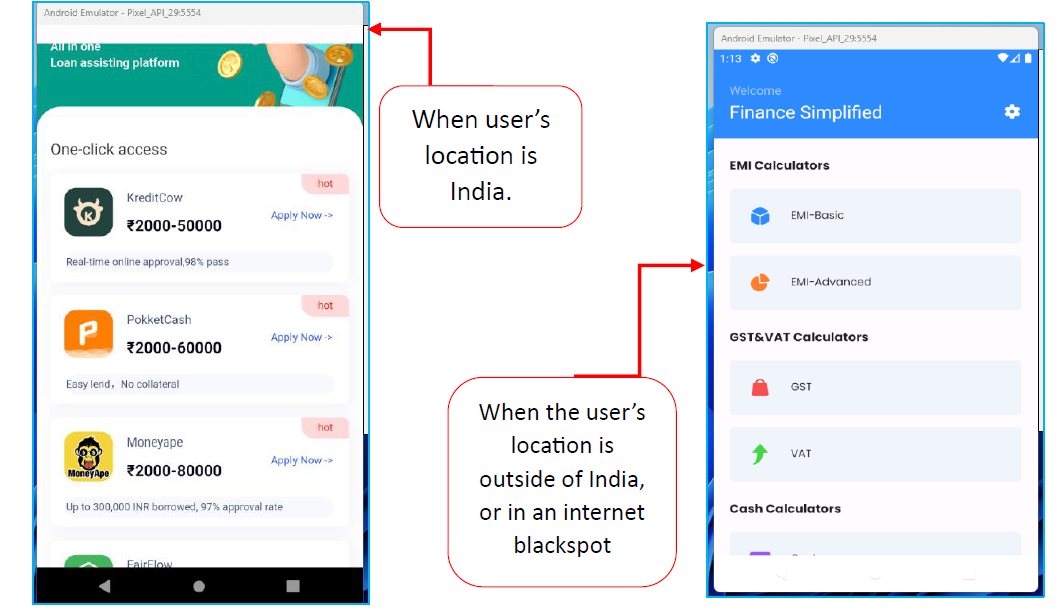
The app, also referred to as “SpyLend,” disguises itself as a financial management tool but actually serves as a gateway to unauthorized loan applications.
These loan apps operate within a WebView, bypassing Google Play Store security checks, and are designed to target Indian users specifically.
Malicious Activities and Distribution
The “Finance Simplified” app has experienced a rapid increase in downloads, reaching over 100,000 installations in a short period.
Despite its seemingly innocuous purpose, the app collects and misuses user data, including photos, videos, contacts, call logs, and SMS messages.
It also captures clipboard content, potentially exposing sensitive information like passwords and credit card details.
The app redirects users to external websites to download additional loan APKs, bypassing the Play Store’s security measures.
According to the Cyfirma Report, this behavior allows attackers to extort money from users by threatening them with manipulated photos and blackmail.
The app’s command and control (C2) infrastructure is hosted on Amazon EC2, with an admin panel supporting English and Chinese languages, suggesting involvement by Chinese-speaking attackers.
The malicious activities are facilitated through various APIs that enable file uploads, data exfiltration, and access to sensitive user information.
User reviews on the Google Play Store highlight complaints about blackmailing, harassment, and data misuse, indicating the app’s involvement in malicious activities.
Security Risks
The presence of such malicious apps on official platforms underscores the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Users are advised to avoid downloading apps from untrusted sources and to carefully review app permissions.
Organizations should implement threat intelligence, deploy robust endpoint security solutions, and conduct regular vulnerability assessments to mitigate risks.
Additionally, users should remain vigilant about social engineering tactics and keep their devices updated with the latest security patches.
Collaboration between app stores and cybersecurity firms is crucial for identifying and removing malicious apps that masquerade as legitimate tools.