Cybersecurity researchers at Push Security have uncovered a sophisticated phishing campaign that exploits Microsoft’s Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) to create legitimate-looking login URLs that redirect users to malicious credential-harvesting sites.
This attack represents a significant escalation in phishing techniques, effectively turning Microsoft’s own infrastructure into an unwitting accomplice in credential theft operations.
The attack begins with malvertising campaigns targeting users searching for Microsoft Office services.
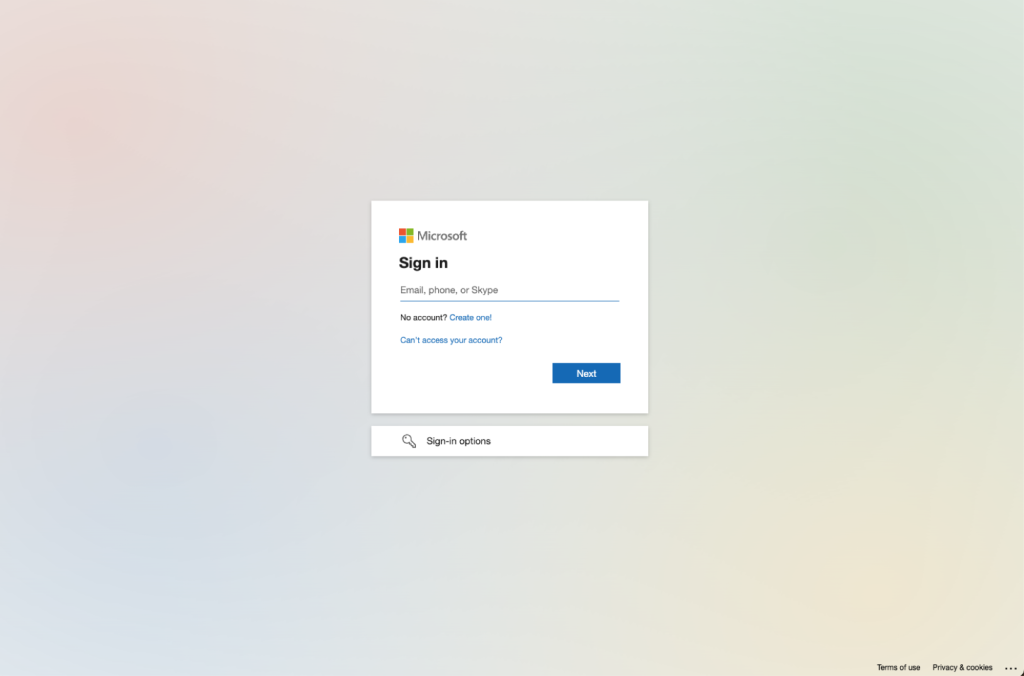
Victims clicking on malicious Google ads are redirected through a complex chain that ultimately leads to authentic-looking Microsoft login pages designed to steal credentials and bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) through adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) techniques.
Novel ADFS Exploitation Creates Legitimate Redirect Chains
The attackers’ innovation lies in their abuse of Microsoft’s ADFS infrastructure. By creating custom Microsoft tenants with ADFS configured, threat actors can generate legitimate office.com URLs that Microsoft’s servers will redirect to attacker-controlled domains.
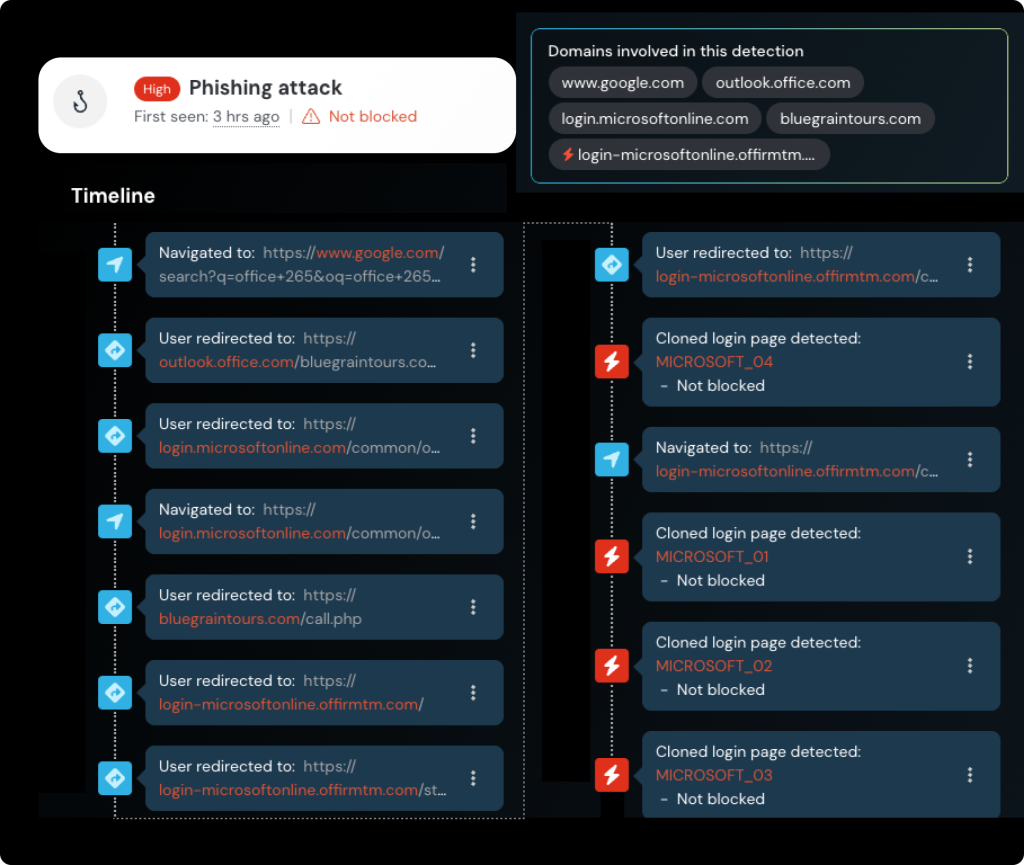
This technique, dubbed “ADFSjacking” by researchers, mirrors the previously documented SAMLjacking attack but exploits Microsoft’s federation services instead.
“This is essentially an open redirect vulnerability,” explained the Push Security research team. “The attacker found a way to redirect from a legitimate outlook.office.com link to a phishing Website.”
The attack leverages fake domains like bluegraintours[.]com, which appears to be an AI-generated travel blog designed to evade domain categorization systems used by security tools.
The phishing sites themselves employ reverse-proxy configurations to intercept user sessions during authentication, effectively stealing both credentials and session tokens to bypass MFA protections.
Conditional loading techniques prevent automated analysis tools from fully recreating the attack flow, adding another layer of evasion.
Detection Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
This attack methodology poses significant challenges for traditional URL-based detection systems, as the initial redirect originates from legitimate Microsoft infrastructure.
Organizations using proxy-based security solutions may struggle to identify malicious activity since the attack chain begins with trusted Microsoft domains.
Security teams can implement several defensive measures to counter these attacks. Monitoring proxy logs for suspicious ADFS redirects, particularly those directing to unauthorized domains with /adfs/ls/ in the path, can help identify potential threats.
Organizations should also monitor for Google redirects to office.com containing advertisement parameters, which may indicate malvertising-based attacks.
Deploying enterprise-wide ad blockers can reduce exposure to malvertising campaigns, though attackers continue to diversify their delivery methods beyond traditional advertising channels.
The attack highlights the growing sophistication of phishing operations and the need for behavior-based detection systems that can identify malicious activity regardless of the delivery mechanism or infrastructure abuse employed by threat actors.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates