A critical security flaw, CVE-2025-6514 (CVSS 9.6), has been discovered in the widely used mcp-remote project, a proxy tool enabling Large Language Model (LLM) hosts—such as Claude Desktop—to communicate with remote Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers.
According to thr report, this vulnerability allows an attacker to execute arbitrary OS commands on any machine running a vulnerable version of mcp-remote. When it connects to a malicious or compromised MCP server, potentially result in a complete system takeover.
The affected versions are 0.0.5 through 0.1.15. The issue has been fixed in version 0.1.16. Users running older versions and connecting to untrusted or insecure MCP servers are at immediate risk.
On Windows, attackers can execute shell commands with full parameter control; on macOS and Linux, arbitrary executables can be run, though with more limited parameter manipulation.
The vulnerability is exploited when a malicious MCP server responds with a specially crafted OAuth authorization_endpoint URL during the authentication process.
Instead of a legitimate URL, the attacker supplies a value that, when processed by mcp-remoteTriggers command execution on the client’s operating system.
For example, on Windows, this could lead to the launch of calc.exe Or even more dangerous commands if further crafted.
Why You Shouldn’t Connect to Untrusted MCP Servers
The risk is not theoretical: two main attack scenarios have been demonstrated:
- Direct Connection to a Malicious Server: An MCP client connects to an attacker-controlled or hijacked MCP server via
mcp-remote, leading to immediate exploitation. - Man-in-the-Middle Attacks on Insecure Networks: If an MCP client connects to a server using an insecure (HTTP) connection, attackers on the same network can intercept and manipulate the traffic, injecting malicious responses that exploit the vulnerability.
Given the growing adoption of remote MCP servers—enabling multiple LLM applications to share resources and simplifying server management—the use of mcp-remote has become widespread across the AI community.
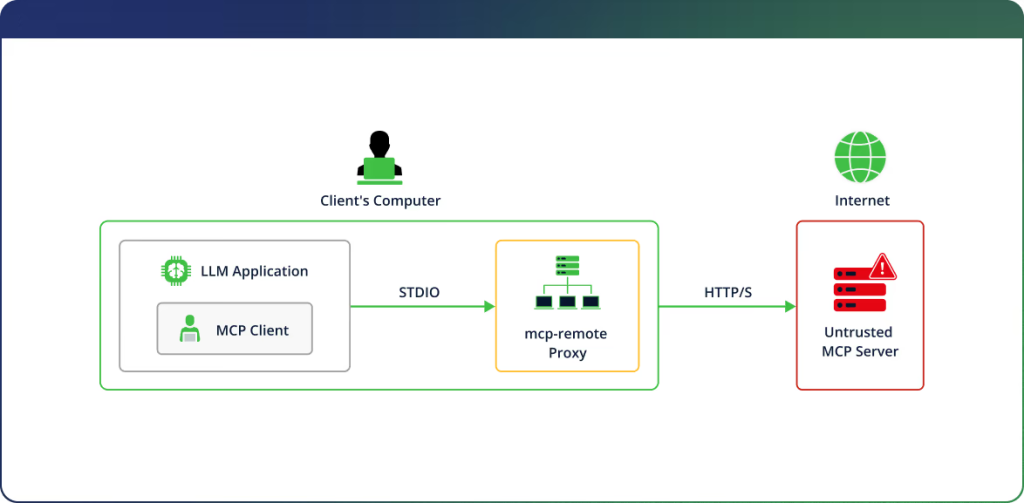
Its integration is documented in official guides from Cloudflare, Auth0, and Hugging Face.
Mitigation steps include:
- Update immediately to
mcp-remoteversion 0.1.16 or later. - Only connect to trusted MCP servers and always use secure (HTTPS) connections.
With LLM hosts like Cursor, Windsurf, and Claude now supporting direct remote MCP connections, the attack surface is expanding.
Users and organizations must remain vigilant, ensuring their configurations do not expose them to similar threats in the evolving MCP ecosystem.
For ongoing updates and detailed technical breakdowns, refer to the JFrog Security Research Center.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get More Instant updates