Trustwave SpiderLabs researchers have uncovered a sophisticated EncryptHub campaign that weaponizes social engineering tactics alongside exploitation of a critical Microsoft Management Console vulnerability to compromise organizational networks.
The threat group, also known as LARVA-208 and Water Gamayun, has evolved its attack methodology to abuse the legitimate Brave Support platform for payload delivery while exploiting CVE-2025-26633 to execute malicious code.
Social Engineering Meets Technical Exploitation
The attack begins with threat actors impersonating IT support staff through Microsoft Teams requests to establish remote connections with targets. Once access is gained, attackers deploy a PowerShell command that downloads and executes malicious payloads from compromised infrastructure.
The campaign leverages the recently disclosed CVE-2025-26633 vulnerability, dubbed “MSC EvilTwin,” which allows execution of malicious .msc files through the Microsoft Management Console.
The exploitation process involves dropping two identically named .msc files – one benign and one malicious – with the malicious version placed in the MUIPath directory.
When the legitimate file executes, the vulnerability causes mmc.exe to load and run the malicious version instead, effectively hijacking the execution flow. SpiderLabs notes that while the vulnerability was officially disclosed in March 2025, related samples were observed as early as February 2025.
Advanced Toolset and Infrastructure Abuse
EncryptHub has expanded its arsenal with sophisticated tools, including SilentCrystal, a Golang-compiled loader that mirrors PowerShell functionality while uniquely abusing Brave Support for payload hosting.
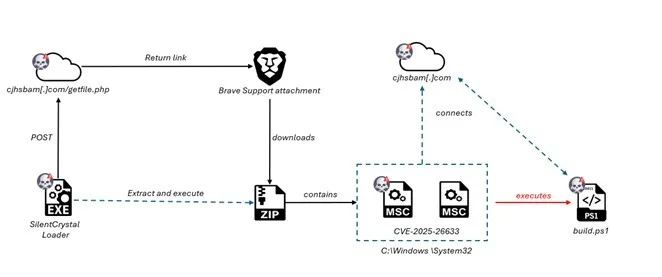
The malware creates deceptive directories at “C:\Windows \System32” with trailing spaces to mimic legitimate system folders and bypass security mechanisms.
The campaign also employs a SOCKS5 proxy backdoor operating in dual modes – client connections to command-and-control servers and server mode for establishing proxy infrastructure.
The malware sends status confirmations via Telegram, including machine information, network details, and geolocation data retrieved from external services.
Researchers discovered a fake video conferencing platform at rivatalk.net, registered in July 2025, which requires access codes to download malicious Windows applications.
This tactic restricts analyst access while ensuring only targeted users can retrieve the payload. The platform distributes setup.msi installers that abuse Symantec’s Early Launch Anti-Malware binary for DLL sideloading attacks.
Growing Threat Landscape
As of February 2025, EncryptHub has reportedly compromised 618 organizations worldwide, demonstrating the campaign’s significant reach and impact.
The threat group’s evolution from targeting Web3 developers to abusing gaming platforms like Steam indicates expanding operational scope and increasing sophistication.
Trustwave SpiderLabs emphasizes the critical need for layered defense strategies, ongoing threat intelligence, and comprehensive user awareness training to combat these adaptive adversaries who combine social engineering with technical exploitation for maximum impact.
IOCs

Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates