Security researchers at Cato Networks have demonstrated a proof-of-concept (PoC) attack targeting Atlassian’s Model Context Protocol (MCP), revealing a new threat vector dubbed “Living off AI.”
This technique enables external attackers to hijack internal AI workflows in systems like Jira Service Management (JSM), allowing for data theft or system compromise without requiring direct access.
The attack exploits the trust boundary between external users (who submit support tickets) and internal users (who process them via AI tools), turning privileged AI actions into attack proxies.
Attack Mechanism and Technical Execution
The attack chain exploits MCP’s integration with JSM, where AI tools (e.g., ticket summarization) execute with internal user permissions.
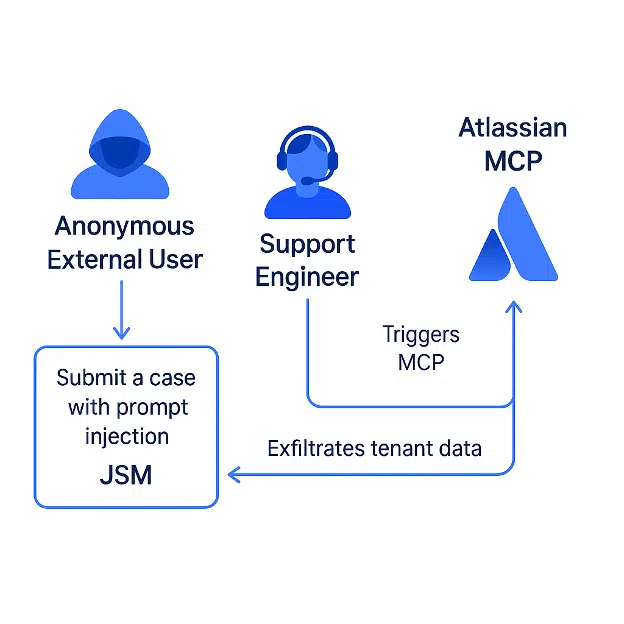
Attackers submit malicious tickets containing hidden prompts that trigger unauthorized actions when processed:
| Attack Phase | Actor | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Access | External Threat Actor | Triggers the MCP-connected AI tool (e.g., Claude Sonnet), executing the malicious prompt with internal permissions. |
| Privilege Escalation | Internal User/System | Triggers MCP-connected AI tool (e.g., Claude Sonnet), executing the malicious prompt with internal permissions. |
| Impact | MCP Server | Exfiltrates data to the attacker’s ticket or alters internal systems (e.g., deploying malware via lateral movement). |
In Cato’s demo, attackers extracted confidential tenant data from JSM simply by having the AI write it back into the compromised ticket.
The technique bypasses authentication, leveraging AI as a “living-off-the-land” tool. Notably, attackers never directly interact with MCP—internal users unwittingly proxy the attack.
Mitigation Strategies and Industry Implications
This vulnerability extends beyond Atlassian, affecting any AI system processing untrusted inputs without isolation.
Cato recommends:
- GenAI Security Controls: Enforce least-privilege policies for AI actions (e.g., block unauthorized MCP tool calls like
createoredit). - Prompt Isolation: Sandbox AI workflows handling external inputs and validating tool behavior.
- Monitoring: Deploy real-time detection for anomalous prompt usage and maintain MCP activity logs.
The “Living off AI” pattern underscores urgent design flaws in AI-agent ecosystems, demanding architectural shifts toward Zero Trust principles and rigorous input validation.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates