The FortiGuard Incident Response (IR) team has revealed that financially motivated adversaries dominated incident patterns during the first half of 2025, emphasizing the continued abuse of legitimate credentials and remote management tools over traditional malware-heavy intrusions.
According to Fortinet’s H1 2025 FortiRecon Threat Intelligence Report, attackers are consistently opting for stealthy and low-complexity intrusion methods, relying on valid user logins and legitimate remote access channels to blend in with normal business operations.
The report highlights that while AI-enabled cyberattacks attract significant attention, FortiGuard’s investigations found little evidence suggesting adversaries’ effective operational use of AI.
Instead, credential-based breaches and misuse of remote access remain the leading initial access vectors observed across multiple industries.
Legitimate Tools, Illegitimate Intent
The FortiGuard team identified several recurring initial access methods: compromised credentials, exposed VPN services, and exploitation of public-facing applications through n-day vulnerabilities.
Once inside, actors deployed legitimate remote management tools like AnyDesk, Atera, Splashtop, and ScreenConnect to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data manually.
These tools, often whitelisted by enterprise environments, enable threat actors to avoid endpoint detection systems that focus on conventional malware signatures.
In one notable case, a ransomware operator accessed a corporate network using stolen VPN credentials on a system lacking multi-factor authentication. From there, the attacker extracted cached hypervisor credentials via browser data and encrypted the company’s virtual machines.
Another case involved a nation-state-affiliated adversary deploying AnyDesk across enterprise systems using a stolen domain administrator account, masking malicious activity within standard IT operations. In both scenarios, adversaries achieved full network access without exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities.
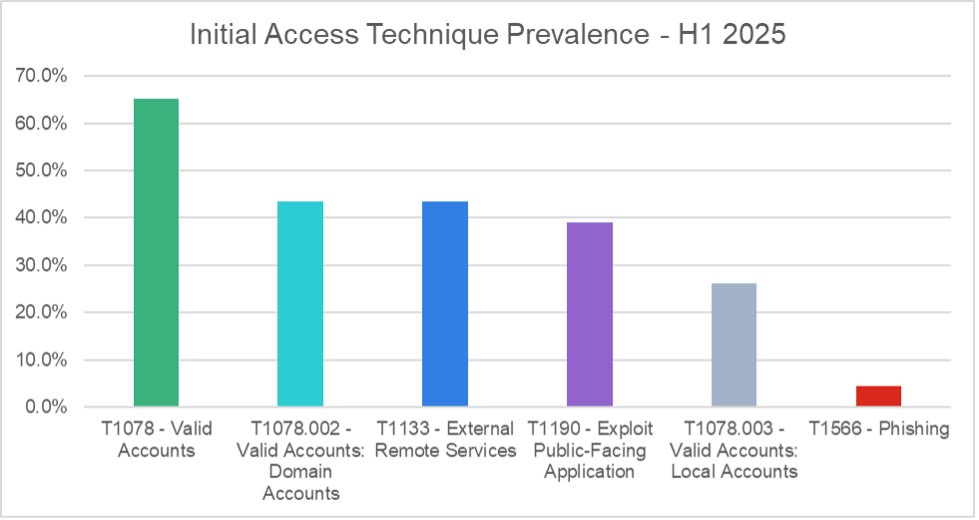
FortiGuard’s forensic analysis revealed that attackers frequently used credential dumping techniques including Mimikatz and Zerologon (CVE-2020-1472) exploitation to escalate privileges.
Data exfiltration was often conducted through manual drag-and-drop operations within RDP sessions, complicating detection since traditional data loss prevention mechanisms fail to capture such interactions.
Defending Against Credential Abuse
Fortinet recommends defenders shift toward identity- and behavior-driven detections rather than relying solely on endpoint protection tools.
Security controls such as internal MFA enforcement, conditional access policies, and baseline monitoring for anomalous account activity are key strategies to counter this threat. Additionally, restricting or monitoring installation of RMM tools can help detect unauthorized persistence mechanisms.
The overarching lesson is clear: attackers no longer need to hack their way in they log in. FortiGuard warns that credential theft and the misuse of legitimate tools represent critical blind spots in enterprise security.
Strengthening identity protections and network visibility remains the most effective countermeasure against these covert, financially motivated threats.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates