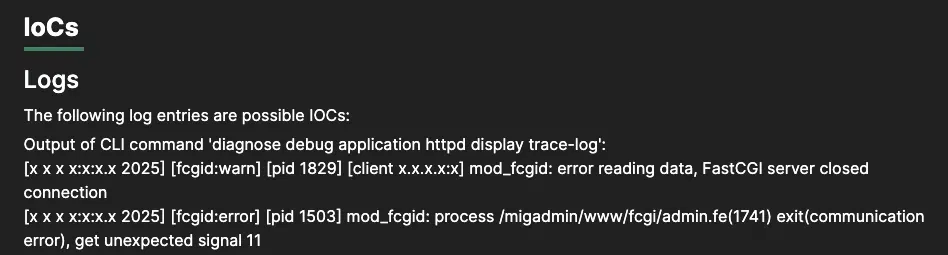
Security researchers have published a detailed technical analysis and proof-of-concept exploit for CVE-2025-32756, a critical zero-day vulnerability affecting multiple Fortinet products that is currently being exploited by threat actors in the wild.
The vulnerability, disclosed by FortiGuard Labs on May 13, 2025, represents a stack-based buffer overflow in administrative APIs that enables unauthenticated remote code execution across several enterprise security products.
CVE-2025-32756 affects a wide range of Fortinet products including FortiCamera, FortiMail, FortiNDR, FortiRecorder, and FortiVoice systems.
FortiGuard Labs confirmed in their advisory that Fortinet has observed active exploitation of this vulnerability in production environments, prompting the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to add the flaw to their Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog on May 14, 20251.
The vulnerability stems from insufficient bounds checking in the APSCOOKIE session management mechanism used by Fortinet’s administrative interfaces.
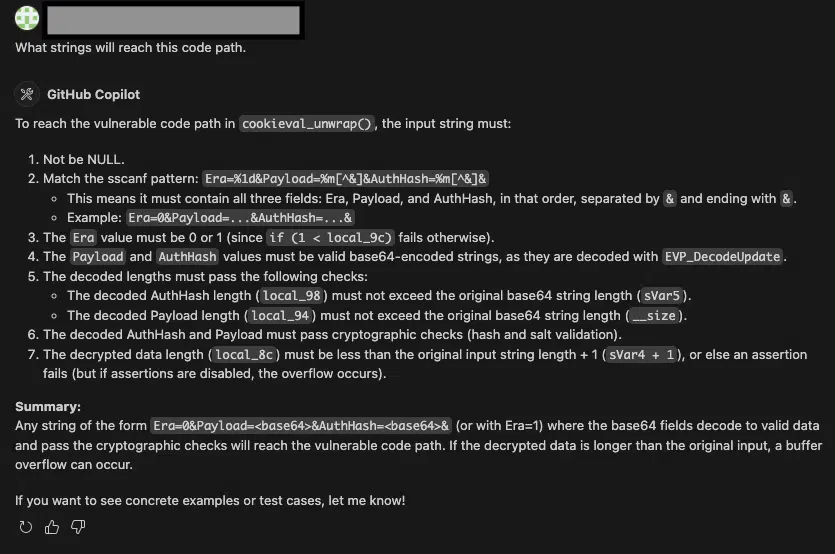
Specifically, the flaw exists in the cookieval_unwrap() function within the libhttputil.so shared library, where user-supplied AuthHash values are processed without proper size validation.
This oversight allows attackers to trigger a stack-based buffer overflow by sending specially crafted base64-encoded data that exceeds the allocated 16-byte buffer.
The technical impact is severe, as successful exploitation provides attackers with complete control over the target system.
The overflow overwrites critical stack data including saved registers and the return address, enabling arbitrary code execution with administrative privileges.
Given that these products are commonly deployed as network security appliances with elevated access to organizational infrastructure, the potential for lateral movement and data exfiltration is significant.
Technical Analysis and Proof of Concept
Independent security researchers conducted a comprehensive analysis of the vulnerability by reverse-engineering both patched and unpatched versions of affected Fortinet products.
Their investigation revealed that the vulnerability could be reliably triggered through HTTP requests to the /module/admin.fe endpoint, making it accessible to remote attackers without authentication requirements.
The research team utilized advanced reverse engineering tools including Ghidra and artificial intelligence assistance to identify the root cause of the vulnerability.
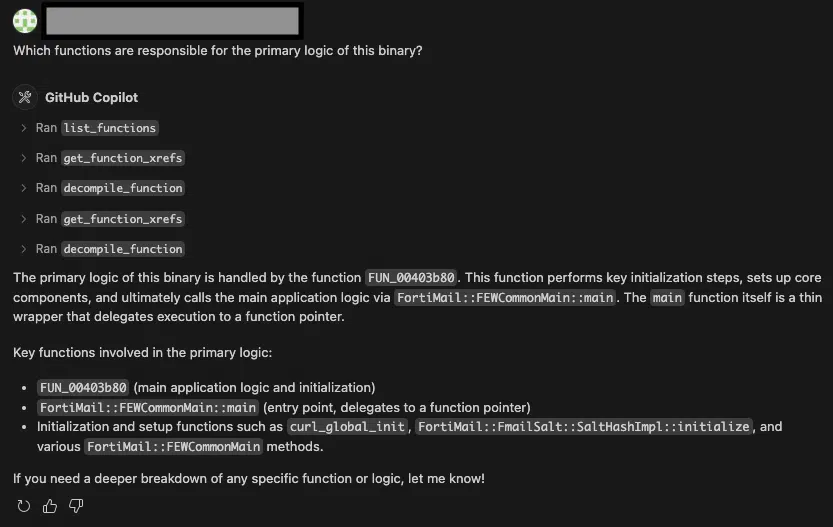
Their analysis demonstrated that the patched version includes a critical size check limiting AuthHash input to less than 30 characters, while the vulnerable version processes arbitrarily large inputs directly.
This simple but crucial difference prevents the buffer overflow condition that enables code execution.
The researchers successfully developed a proof-of-concept exploit demonstrating reliable control over the instruction pointer, though they have elected not to publish a fully weaponized exploit given the active exploitation in the wild.
Their technical writeup provides sufficient detail for security professionals to understand the vulnerability mechanics while avoiding materials that could facilitate additional attacks.
Patching Recommended as Exploitation Continues
Security experts strongly recommend immediate application of available patches or implementation of mitigation strategies outlined in FortiGuard Labs’ advisory.
The combination of active exploitation, remote accessibility, and the widespread deployment of affected products creates an urgent security situation for organizations relying on Fortinet infrastructure.
The vulnerability has been integrated into automated penetration testing platforms, indicating its potential for inclusion in attacker toolkits.
Organizations should prioritize updating affected systems and monitor for indicators of compromise detailed in the FortiGuard advisory to detect potential exploitation attempts.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates