Google’s Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) has released new technical guidance to counter UNC6040, a financially motivated threat cluster exploiting voice phishing to compromise Salesforce environments.
Instead of exploiting application vulnerabilities, the group has successfully relied on convincing phone-based social engineering to trick employees into authorizing malicious connected applications, giving them wide access to valuable corporate data.
These campaigns continue to demonstrate the rising risks of identity abuse across SaaS platforms, where human manipulation circumvents strong platform security baselines.
UNC6040’s Attack Flow
UNC6040 operations typically begin with vishing calls that impersonate IT or vendor support staff. Through these calls, employees are persuaded to visit Salesforce’s connected app setup page and authorize what appears to be a legitimate Salesforce tool, such as a modified version of the Data Loader application.
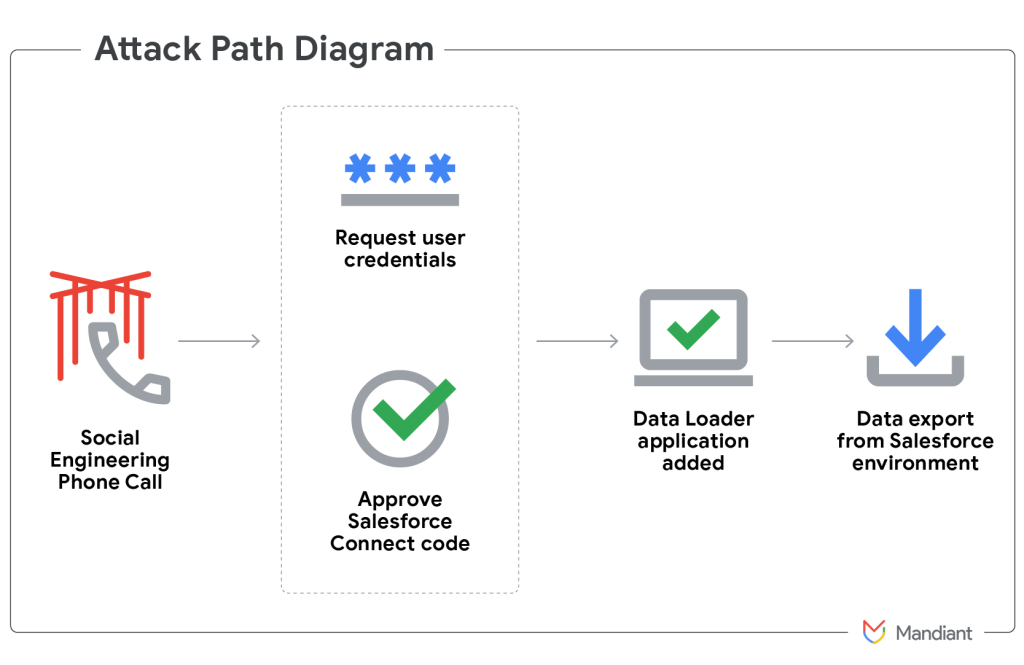
Once granted access, the fraudulent app allows threat actors to retrieve sensitive records at scale using Salesforce API functions, query bursts, and bulk report exports. This unauthorized activity enables attackers to access customer data, contact information, or financial datasets within minutes.
In multiple incidents, attackers subsequently expanded access by pivoting into connected platforms such as Okta and Microsoft 365, where they exfiltrated emails, documents, and identity data.
Google notes that the infrastructure used during these intrusions often involves Mullvad VPN ranges, which obfuscate the origin of exfiltrated traffic.
Google and Mandiant Recommendations
The guidance focuses on strengthening defenses across identity security, Salesforce application hardening, and event monitoring. For identity protection, Google stresses requiring phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication, preferably using FIDO2 security keys for administrator-level accounts.
Organizations should centralize user access through corporate-managed Single Sign-On platforms while restricting elevated actions to trusted and company-managed devices.
In addition, help desk procedures must adopt high-assurance verification methods, such as live video ID proofing, before granting password resets or MFA changes, to ensure that attackers cannot bypass controls by impersonating employees.
In terms of Salesforce configuration, organizations are advised to enforce strict login IP restrictions, adopt “deny by default” rules for connected app and API access, and limit the “API Enabled” permission to only a handful of vetted users.
Session settings can be aligned to require high-assurance authentication for sensitive operations such as exporting reports or conducting large-scale queries.
Privilege assignments should follow the principle of least privilege, with careful elimination of broad permissions, such as “View All Data” or “Modify All Data.” Complementing these policies, Salesforce’s Security Health Check tool provides a fast means to identify configuration gaps continuously.
Detection and Monitoring Enhancements
GTIG highlights that logging and monitoring remain crucial for detecting UNC6040 techniques in real-time. Organizations should enable Salesforce Shield’s Event Monitoring features to gain visibility into login behavior, API usage, bulk data exports, and report downloads.
Detection baselines should focus on identifying suspicious OAuth authorizations followed quickly by large-scale record downloads, anomalous API query bursts, or sensitive report exports conducted by accounts not associated with legitimate integrations.
Coordinated monitoring across Salesforce, Okta, and Microsoft 365 allows correlation of suspicious logins and data pulls from the same untrusted VPN egress IPs.
By linking Salesforce OAuth activity with subsequent activity in other SaaS platforms, security teams can rapidly uncover lateral movement consistent with UNC6040 operations.
Through stronger authentication processes, tightened Salesforce governance, and real-time anomaly detection, Google’s guidance aims to provide organizations with a layered framework that addresses UNC6040’s reliance on social engineering.
As attackers shift from traditional exploits to trust-based manipulation, defenders are urged to modernize their SaaS security posture, ensuring human factors are protected as rigorously as technical perimeters.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates