A critical new vulnerability in the HTTP/2 protocol, dubbed “MadeYouReset” (CVE-2025-8671), has been publicly disclosed, posing significant denial-of-service risks to web servers worldwide.
The vulnerability was revealed on August 13, 2025, by security researchers who warned that it can bypass existing protections and render servers completely unavailable to legitimate users.
Sophisticated Attack Builds on Previous Exploit
The MadeYouReset vulnerability represents an evolution of the devastating “Rapid Reset” attack that emerged in 2023, which was described as “the largest DDoS attack to date” by major cloud providers.
However, this new threat circumvents the mitigation strategies that were successfully deployed against its predecessor, making it particularly dangerous for organizations that believed they were protected.
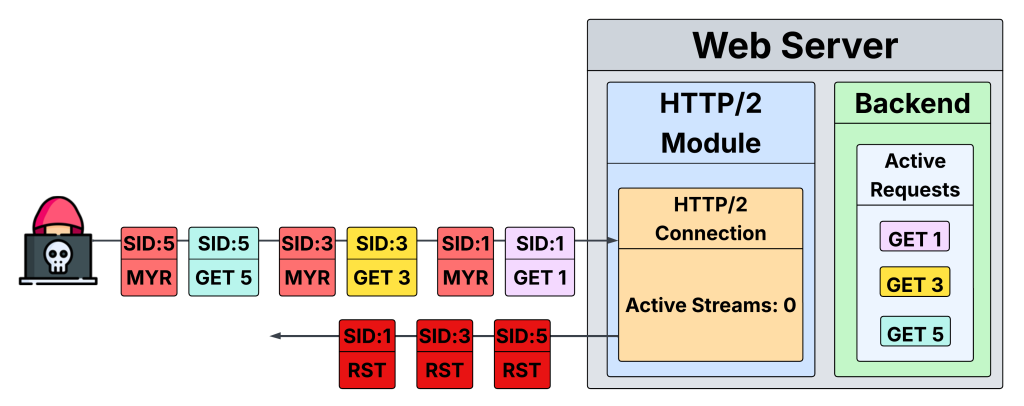
The attack exploits HTTP/2’s built-in concurrency mechanisms by allowing malicious actors to create “effectively unbounded concurrent work on servers by bypassing HTTP/2’s built-in concurrency limit”.
Unlike traditional denial-of-service attacks that require substantial resources, MadeYouReset enables attackers to cause maximum disruption with minimal effort, creating the asymmetric cost imbalance that makes such vulnerabilities so effective.
Technical Innovation Sidesteps Common Defenses
The vulnerability’s creators discovered six different methods to trigger server-initiated stream resets, eliminating the need for attackers to send cancellation requests themselves.
This clever approach completely bypasses the rate-limiting controls that organizations implemented to defend against Rapid Reset attacks.
“Instead of the client canceling a request, can we make the server cancel it for us?” the researchers explained, describing their innovative approach.
By crafting specific invalid control frames or violating protocol sequencing at strategic moments, attackers can force servers to generate RST_STREAM frames while backend systems continue processing requests.
Widespread Impact Across Major Platforms
The vulnerability affects numerous popular web server implementations and platforms. Confirmed affected projects include Netty (CVE-2025-55163), Apache Tomcat (CVE-2025-48989), F5 BIG-IP (CVE-2025-54500), h2o, and swift-nio-http2.
The researchers note that most affected servers can be driven into complete denial-of-service, with some experiencing out-of-memory crashes.
The research was conducted jointly by Prof. Anat Bremler-Barr and Yaniv Harel from Tel Aviv University, with partial support from Imperva.
The disclosure process involved coordination across more than 100 vendors through CERT/CC, highlighting the vulnerability’s extensive reach across the internet infrastructure.
Organizations running HTTP/2-enabled web servers should review vendor advisories and apply available patches immediately.
The vulnerability’s ability to bypass existing Rapid Reset mitigations means that servers previously considered protected may now be vulnerable to this new attack vector.
Security teams should monitor for unusual patterns of concurrent requests and implement additional rate-limiting measures as interim protections while permanent fixes are deployed.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates