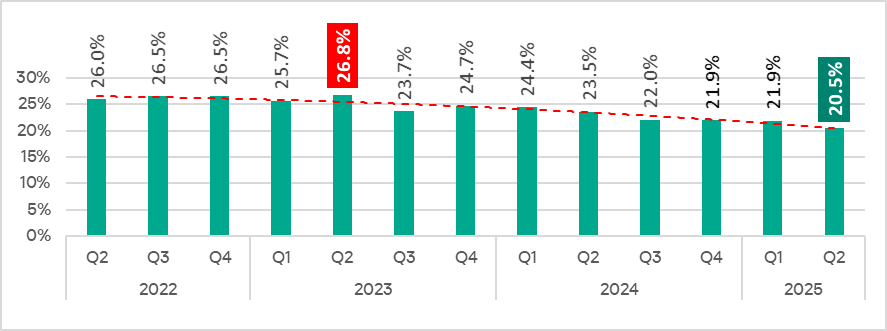
In Q2 2025, the percentage of industrial control system (ICS) computers on which malicious objects were blocked fell to 20.5%, marking a 1.4 percentage point decline from the previous quarter and a 3.0 percentage point decrease compared to Q2 2024, according to Kaspersky’s latest ICS threat landscape report.
Despite the overall decline, cybersecurity risks in the industrial sector remain significant, particularly due to malicious scripts and phishing campaigns targeting operational environments.
Rising Role of Malicious Scripts and Phishing Pages
While overall infection rates declined, malicious scripts and phishing activity continue to play an outsized role in attempted compromises of ICS environments.
The report highlights that malicious scripts and phishing pages targeted 6.49% of all ICS computers in Q2 2025, a notable reduction of 0.67 percentage points from the previous quarter. However, these types of threats remain one of the most persistent initial infection vectors.
Attackers often leverage malicious scripts embedded in compromised websites, phishing emails, or cloud-based services to gain an initial foothold within operational technology networks.
Once executed, these scripts serve as enablers for multi-stage attacks, creating communication links with external command-and-control (C2) servers and facilitating lateral movement.
Through this entry point, adversaries gain the ability to escalate privileges, infect additional systems, and prepare for delivery of next-stage payloads such as spyware, cryptominers, or ransomware.
The report notes that phishing campaigns remain highly effective against industrial operators, particularly when they employ malicious documents and links to compromised websites.
Email-borne threats, including macro-enabled documents and counterfeit login pages, showed increased activity across almost all regions and contributed to compromises in industries such as energy, manufacturing, and chemical processing.
Initial Infection and Next-Stage Malware
In terms of initial infection activity, denylisted internet resources and malicious documents were the only categories to increase during the quarter.
ICS computers blocking connections to denylisted malicious websites rose to 5.91%, with higher activity detected in Africa (6.98%) and Eastern Europe. Malicious document-based attacks also grew slightly to 1.97%, heavily distributed through spear-phishing campaigns.
By contrast, the activity of next-stage malware decreased across all categories. Spyware detections fell to 3.84%, ransomware activity dropped to 0.14%, and cryptomining attempts receded to some of their lowest levels since mid-2022.
This suggests that while adversaries are successfully deploying malicious scripts and phishing lures, the follow-through with advanced payloads has declined for now.
Despite these reductions, the persistence of phishing and script-based intrusions underscores their strategic role as the first step in complex attack chains. Industrial networks, with their mix of legacy and modern systems, remain vulnerable to these techniques.
Kaspersky’s findings suggest that ICS cybersecurity strategies must continue focusing on phishing resilience, network segmentation, and proactive monitoring of web and scripting activity in OT environments.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates