Cloud environments rely on the Instance Metadata Service (IMDS) to furnish virtual machines with temporary credentials and vital configuration data, eliminating the need to hardcode secrets.
However, this convenience can be weaponized when attackers coerce applications into leaking those very credentials. Recent threat hunting by the Wiz Research team uncovered anomalous IMDS queries that led to the discovery of zero-day exploitation in widely used services.
Their data-driven methodology not only detected abuse of IMDS but also illuminated novel attack vectors leveraged by adversaries seeking initial access to cloud workloads.
Understanding the Risks of IMDS
IMDS provides a local HTTP endpoint on every compute instance—169.254.169.254 in AWS—that serves metadata and short-lived credentials associated with the instance’s IAM role.
AWS offers two versions: IMDSv1, which accepts unauthenticated HTTP GET requests, and IMDSv2, which mandates a session token obtained via an initial PUT request.
Attackers have long targeted IMDSv1 through Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) in web applications, exploiting its lack of request validation to harvest credentials.
Even with IMDSv2, sophisticated adversaries can abuse injection flaws or misconfigured workloads to forge the necessary tokens and headers, but the added complexity significantly raises the bar for successful exploitation.
Organizations are urged to enforce IMDSv2 and implement least-privilege IAM roles to curtail IMDS abuse.
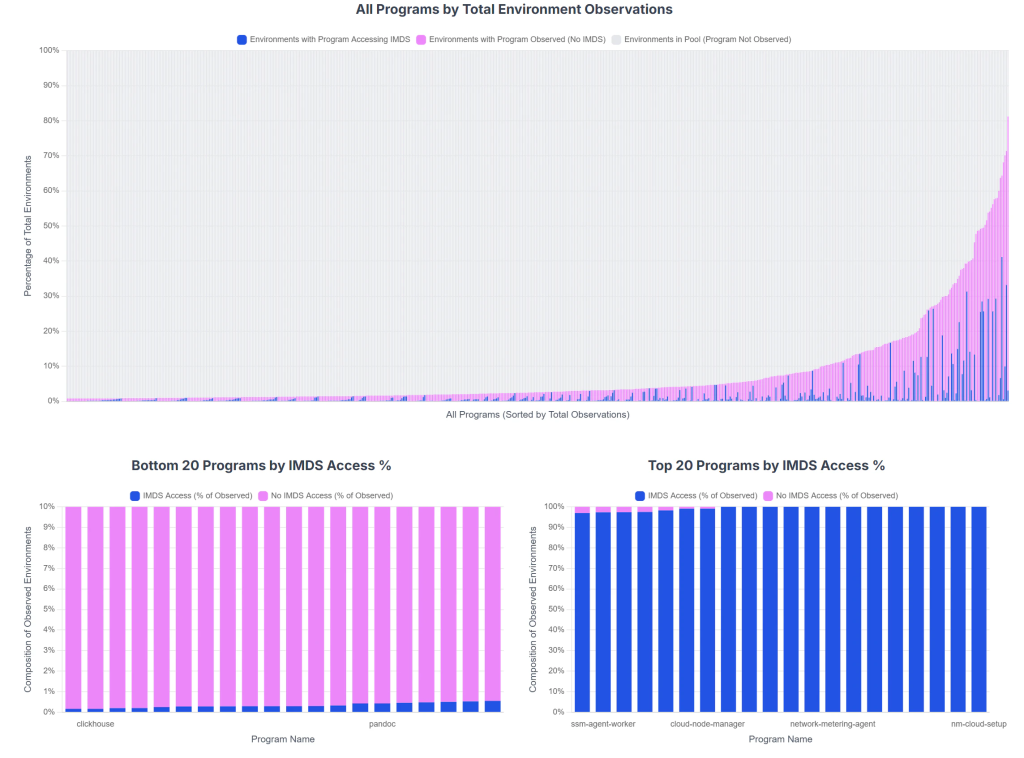
Anatomy of the Attack
Wiz’s runtime sensor aggregates telemetry across thousands of cloud environments to establish a baseline of legitimate IMDS usage by standard SDKs, agents, and utilities.
Suspicious deviations emerge when uncommon processes suddenly query sensitive metadata paths.
In one case, the team identified an unexpected IMDS request from the Pandoc utility—a document converter that should never contact metadata endpoints.
Investigation revealed a previously unknown SSRF flaw (CVE-2025-51591) in Pandoc’s HTML-to-PDF conversion when untrusted <iframe> tags were rendered without sandboxing.
An attacker-hosted HTML document containing a link <iframe> pointing at /latest/meta-data/iam/info attempted to exfiltrate credentials, but mandatory IMDSv2 enforcement thwarted the exploit.
A second finding involved ClickHouse’s SELECT * FROM url feature in a misconfigured deployment. An attacker exploited SSRF to access metadata paths in a GCP environment, aiming to obtain service account tokens.
Although this instance lacked high-privilege credentials, the technique underscores the cloud-agnostic nature of IMDS abuse and the critical need for secure configuration.
Strengthening Defenses
These real-world discoveries emphasize that preventing IMDS exploitation requires both robust configuration management and anomaly-based detection.
Enforcing IMDSv2 across all instances nullifies unauthenticated metadata access attempts. Mapping instance roles to the principle of least privilege limits the impact of any compromised credentials.
Continuous monitoring of IMDS access patterns, especially to sensitive endpoints, helps identify emerging threats before they escalate.
The Wiz platform combines proactive prevention spotting IMDSv1 usage, misconfigurations, and excessive permissions with real-time detection of anomalous metadata requests.
By visualizing attack paths through a security graph, defenders can prioritize high-risk incidents and rapidly remediate vulnerabilities.
IMDS will remain integral to cloud security, but its abuse potential demands vigilant oversight.
Adopting token-based metadata access, adhering to least-privilege principles, and deploying anomaly-driven threat hunting are critical to safeguarding cloud environments against advanced adversaries exploiting IMDS.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get More Instant Updates