A comprehensive security research investigation has revealed critical vulnerabilities across four Intel internal websites that allowed unauthorized access to detailed employee information for more than 270,000 workers worldwide.
Security researcher Eaton discovered multiple authentication bypass techniques and hardcoded credentials that provided extensive access to Intel’s internal systems between October 2024 and February 2025.
Widespread Authentication Failures
The vulnerabilities spanned Intel’s business card ordering system, product hierarchy management platform, product onboarding website, and SEIMS supplier management system.
Each system exhibited fundamental authentication flaws that allowed complete bypass of Microsoft Azure Active Directory single sign-on (SSO) protections through client-side JavaScript manipulation and hardcoded credential exploitation.
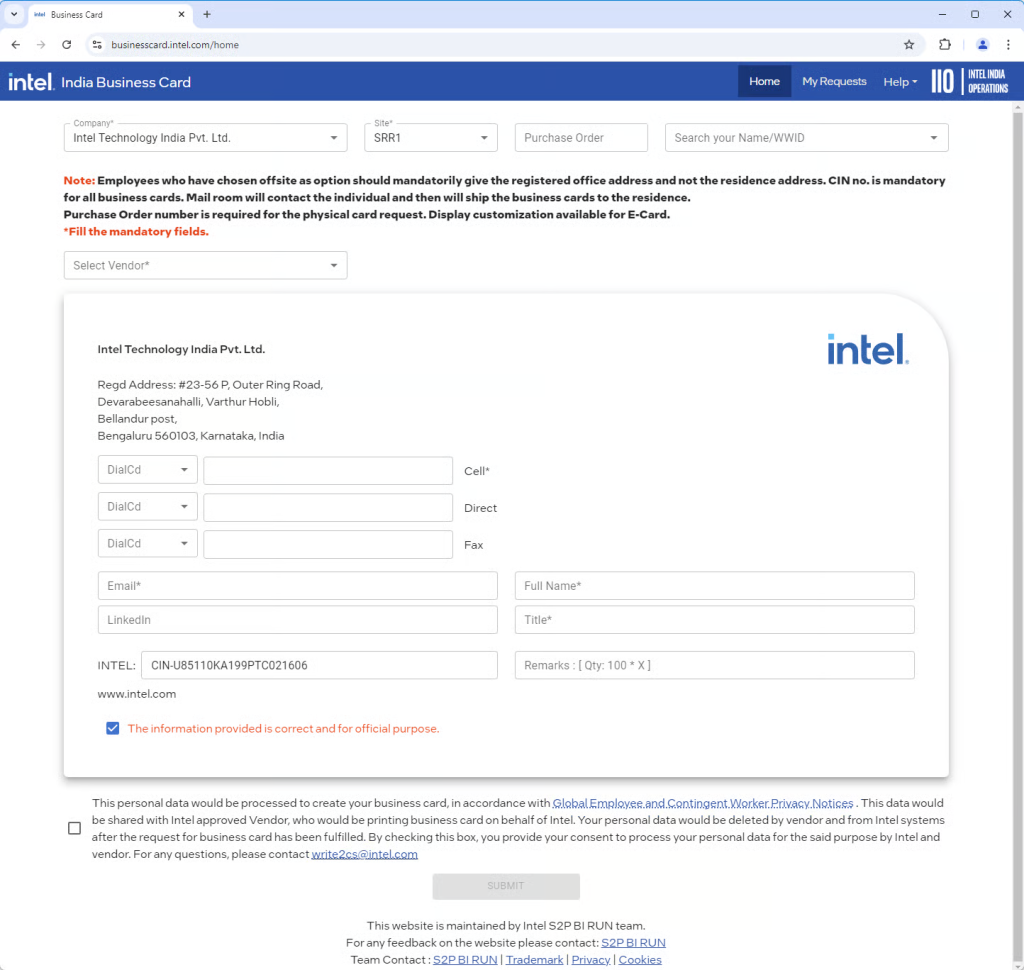
The most significant breach occurred through Intel India Operations’ business card ordering website, where researchers discovered an unauthenticated API endpoint that provided access tokens without proper verification.
By manipulating the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) JavaScript functions and removing API filters, attackers could retrieve a nearly 1GB JSON file containing comprehensive employee data including names, roles, managers, phone numbers, and email addresses.
Technical Analysis of Exploitation Methods
The attack vectors demonstrated a sophisticated understanding of modern web application architectures.
The researcher utilized several techniques, including modifying the getAllAccounts() function to return non-empty arrays, overriding isAuthenticated boolean values, and exploiting client-side role validation mechanisms.
Particularly concerning was the discovery of hardcoded credentials encrypted with weak AES implementations.
The Product Hierarchy website contained credentials protected by client-side encryption using easily decryptable keys, with developers even providing links to decryption websites within the source code.
Multiple systems used predictable credentials, with one system employing “admin/admin123” as administrative access credentials.
Vulnerability Summary by System
| System | Primary Vulnerability | Access Level | Employee Data Exposed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Card Ordering | Unauthenticated API token access | Full employee database | 270,000+ records |
| Product Hierarchy | Hardcoded encrypted credentials | Admin access + employee data | Full workforce |
| Product Onboarding | Multiple hardcoded secrets | Admin access + employee data | Full workforce |
| SEIMS Supplier Site | JWT validation bypass | Admin access + supplier data | Full workforce + NDA details |
Response Timeline and Remediation
Intel’s response to the vulnerability disclosures revealed significant challenges in its security reporting process.
Despite having a well-publicized bug bounty program offering rewards up to $100,000 for hardware vulnerabilities, website security issues fall outside the scope of monetary rewards.
Researchers received only an automated acknowledgment when reporting to Intel’s designated security email address.
The disclosure timeline spanned from October 14, 2024, through August 18, 2025, with all vulnerabilities resolved by February 28, 2025.
Intel recently expanded their bug bounty program to include services coverage, though comprehensive website vulnerability rewards remain limited.
Industry Implications
This incident highlights the persistent challenge of securing internal web applications within large technology corporations.
The combination of client-side authentication bypasses, hardcoded credentials, and inadequate API security demonstrates the need for comprehensive security architecture reviews beyond traditional hardware-focused vulnerability assessments.
The exposure of supplier relationship data through the SEIMS platform particularly raises concerns about supply chain security, as the compromised system contained detailed information about non-disclosure agreements and vendor relationships critical to Intel’s operations.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates