Hello world, hello hackers! We’re Future Sight—your soon-to-be favorite research group.
Never heard of us? Don’t worry, nobody has. This is literally our first drop.
Today, we will make some red teamers happy with a new technique we have discovered that allows an authenticated user in ArgoCD to steal powerful GitHub credentials, further compromising Git accounts and more.
For those who like Kubernetes security, you will enjoy even more! Let’s dive into the world of ArgoCD, Kubernetes, and Git and use the goddamn octopus against itself!
It’s the year 2025, and exfiltration of information is a buzz theme in cybersecurity, especially in those poor password managers.
We want to contribute to that chaos a little bit and raise awareness among everyone in the cybersecurity field by demonstrating a way to exfiltrate Git credentials in ArgoCD and Kubernetes.
ArgoCD is considered by most to be the best tool in GitOps continuous delivery for Kubernetes, ranking first in the CNAF “Continuous Integration & Delivery” landscape.
Similar tools might also allow these attacks, so buckle up, kids; this is going to be an interesting ride!
The Exploit
Kubernetes DNS is the first place a pod looks when resolving a domain. Our attack abuses that behavior to trick ArgoCD’s repository server into connecting to an attacker-controlled service instead of the real GitHub.
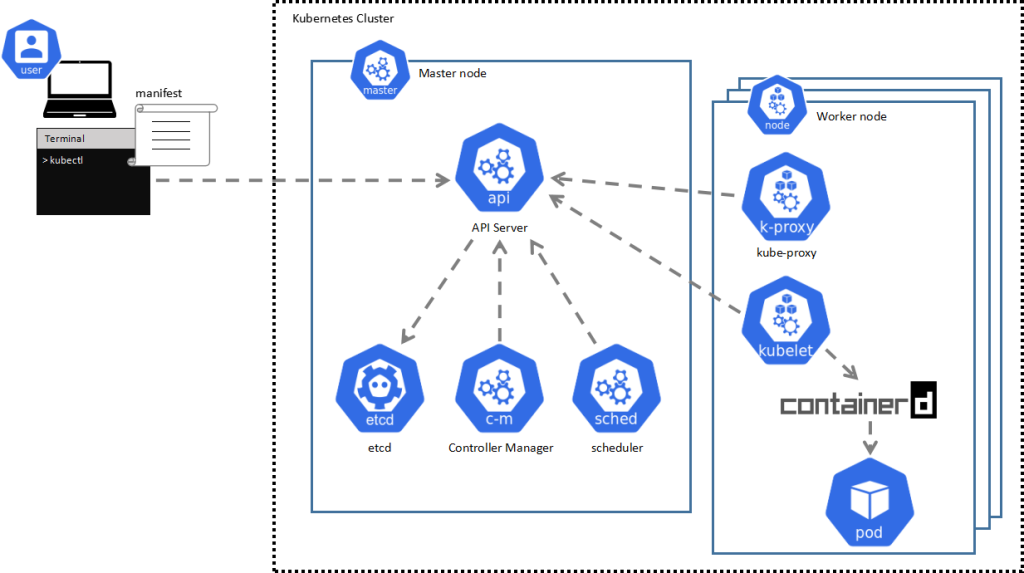
By deploying a malicious Service named github in the com namespace, an adversary can create a DNS record that resolves github.com to their cluster‐internal IP.
When ArgoCD fetches manifests via HTTPS, the attacker adds a custom certificate through ArgoCD’s certificate feature, allowing inspection of the Authorization header and exfiltration of credentials.
Both HTTP(S) Basic auth tokens (for Git or Helm) and GitHub App JWTs or access tokens can be captured.
The attacker then proxies requests to the legitimate GitHub endpoint to maintain operation while silently siphoning credentials.
The compromised ArgoCD account must possess policies to create certificates, read repositories, applications, clusters, and, optionally, view logs.
Once an adversary satisfies these prerequisites, they deploy the malicious Argexfil service, intercept ArgoCD’s Git connections, and log credentials externally.
A proof‐of‐concept script (argexfil_verify.py) is available on our GitHub for verifying permissions and automating the deployment.
Mitigations and Future Work
To defend against this novel attack, apply least‐privilege principles for ArgoCD users, enforce strict project scopes, and monitor internal DNS and pod‐to‐pod traffic.
Restrict certificate creation to administrators and favor SSH connections, which do not leak private keys.
Generate GitHub tokens with minimal scope. Future research may explore injecting malicious YAML manifests, exploiting ArgoCD notifications for exfiltration, or targeting cluster authentication secrets via the same DNS trick.
Similar techniques could impact Flux, CircleCI, and other GitOps platforms.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates