A malicious homoglyph typosquat campaign on NuGet has been caught impersonating Nethereum, the widely used .NET library for Ethereum integration.
Socket’s Threat Research Team uncovered two counterfeit packages of etherеum.All and NethereumNet that embedded hidden exfiltration logic to steal sensitive blockchain wallet data from developers and applications.
Malicious Code Hidden Behind Legitimate Namespaces
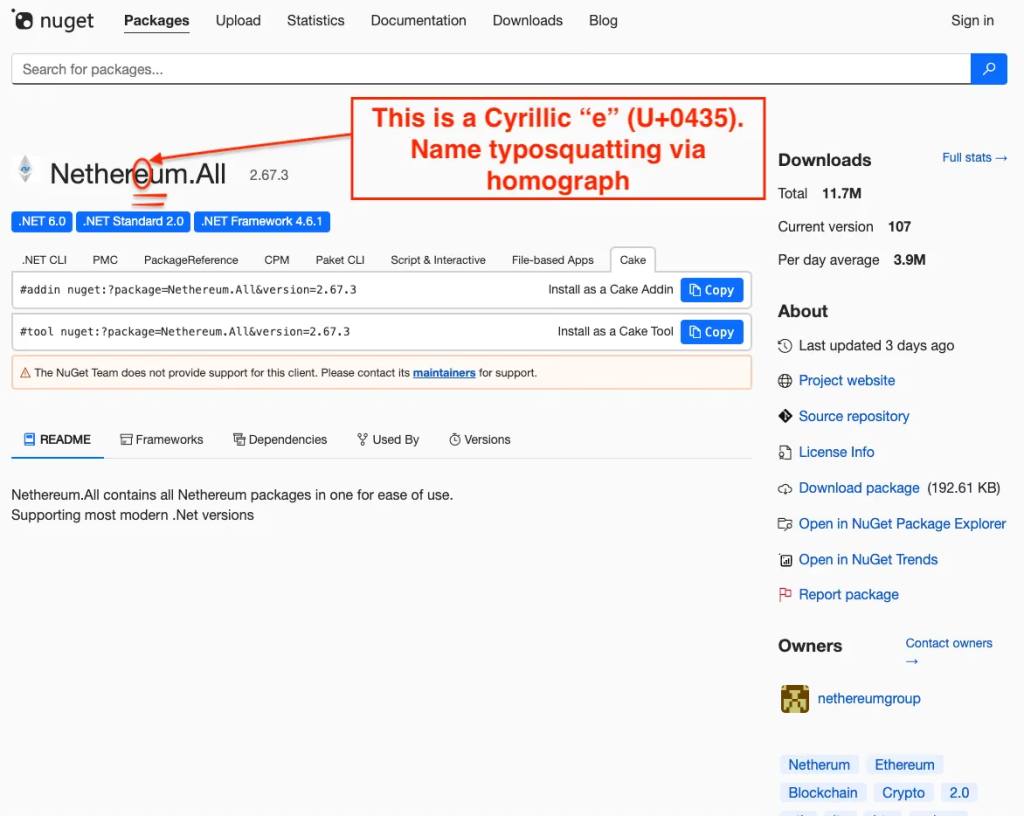
The bogus package Netherеum.All (note the Cyrillic “е”, U+0435) was published on October 16, 2025, under a deceptive publisher name, nethereumgroup. Its title visually mimicked the authentic Nethereum project, tricking users into downloading it.
The package’s download count ballooned to 11.6 million in a single day, evidence of automated download inflation to falsely boost credibility.
According to Socket’s analysis, the malicious code was contained in the EIP70221TransactionService shuffle method.
This function used a 44‑byte XOR mask to decode a hardcoded command‑and‑control (C2) URL that resolved to hxxps://solananetworkinstance[.]info/api/gads at runtime.
When executed, the routine created an HTTPS POST request with a form field named message, used to exfiltrate input strings such as private keys, seed phrases, signed transactions, or keystore JSON data.
The method was embedded within realistic transaction and wallet helper classes that mirrored the actual Nethereum namespaces and imported legitimate dependencies, such as Nethereum.
Signer and Nethereum.RPC. This made infected builds appear normal during compilation, while the Beacon silently transmitted secrets whenever the Shuffle function was reached.
Typosquat and Supply Chain Deception
Socket researchers linked Netherеum all to an earlier clone, NethereumNet, which used identical code and shared infrastructure.
Both packages were uploaded by the same threat actor using two aliases nethereumgroup and NethereumCsharp. The campaign exploited Unicode homoglyphs and inflated download counts to impersonate trusted libraries and appear popular in NuGet search results.
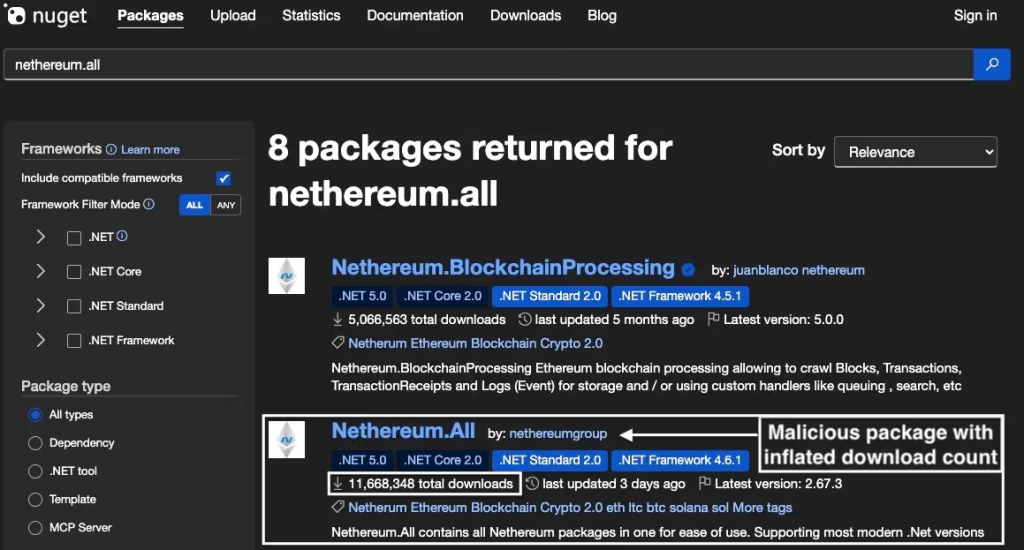
Netherеum.All with 11.6 million total downloads, just days after publication, a hallmark of scripted download inflationThe malicious packages were reported to NuGet on October 18, leading to their removal and the publisher’s suspension on October 20, about 4 days after publication. However, that small window was enough to compromise developer secrets if affected functions were invoked in production or CI pipelines.
Experts warn that similar threats may evolve with deeper obfuscation or install‑time execution through MSBuild or module initializers.
Developers are urged to verify package publishers, monitor dependency changes, scan for hidden network egress, and flag homoglyph‑based names. Socket recommends using its CLI, GitHub App, and Socket Firewall to block malicious dependencies before they reach developer environments.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Malicious Packages
Threat Actor’s NuGet Aliases
nethereumgroupNethereumCsharp
C2 Endpoint
solananetworkinstance[.]info/api/gads
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates