Microsoft has revealed its multi-layered defense strategy against indirect prompt injection attacks, a growing cybersecurity threat targeting large language model (LLM) systems used in enterprise environments.
The company’s Microsoft Security Response Center announced the comprehensive approach on Tuesday, highlighting both preventative and detective measures designed to protect users from sophisticated AI-based attacks that could lead to data theft and unauthorized actions.
Understanding the Emerging Threat
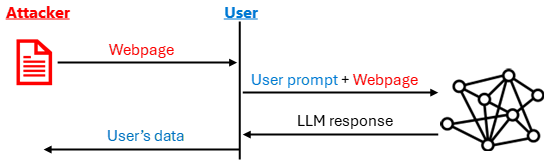
Indirect prompt injection represents a new class of adversarial techniques where attackers embed malicious instructions into external content that LLM systems process on behalf of users.
Unlike direct attacks where hackers target users directly, these sophisticated methods involve injecting hidden commands into webpages, documents, or emails that AI systems later interpret as legitimate instructions.
The technique exploits the instruction-following capabilities of modern AI models, potentially allowing criminals to steal sensitive data or force systems to perform unintended actions.
The security implications are significant, with Microsoft identifying data exfiltration as one of the most concerning potential impacts.
Attackers can manipulate AI systems to extract user conversation history, access documents, or send sensitive information to external servers through various techniques, including HTML image tags, clickable links, or tool-based data transfers.
Additionally, these attacks could force AI assistants to send phishing emails from trusted accounts or execute unauthorized commands with user-level permissions.
Microsoft’s Defense-in-Depth Approach
Microsoft’s security strategy encompasses three primary defensive categories: prevention, detection, and impact mitigation.
The company employs both probabilistic defenses that reduce attack likelihood and deterministic measures that provide absolute protection against specific attack vectors.
For prevention, Microsoft has developed Spotlighting, an innovative technique that helps AI models distinguish between user instructions and potentially malicious external content.
This approach involves three operational modes: delimiting untrusted input with randomized text markers, adding special tokens throughout suspicious content, and encoding external text using algorithms like base64 to separate different input sources.
The detection phase utilizes Microsoft Prompt Shields, a classifier-based system trained to identify prompt injection attempts across multiple languages.
This tool integrates with Microsoft Defender for Cloud, providing enterprise-wide visibility and enabling security teams to correlate AI-related threats with broader attack patterns.
Ongoing Research and Implementation
Microsoft continues advancing foundational research through initiatives like TaskTracker, which analyzes AI model internal states during processing, and the LLMail-Inject challenge that generated over 370,000 test prompts to stress-test defensive systems.
The company has also open-sourced research datasets and collaborated with industry partners to develop standardized design patterns for securing AI agents.
The comprehensive strategy reflects Microsoft’s recognition that indirect prompt injection attacks have become one of the most frequently reported AI security vulnerabilities, earning the top position in the OWASP Top 10 for LLM Applications.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates