FortiGuard Labs has uncovered a sophisticated phishing campaign targeting Japanese users with MostereRAT, a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) that employs advanced evasion techniques and legitimate remote access tools to gain complete control over infected Windows systems.
The malware represents an evolution of a banking trojan first identified in 2020, now transformed into a comprehensive system infiltration tool.
Multi-Stage Attack Chain with EPL Exploitation
The attack begins with carefully crafted phishing emails that mimic legitimate business inquiries sent to Japanese recipients.
Victims are directed to malicious websites that automatically download Word documents containing embedded archives.
Upon execution, the malware deploys a unique payload written in Easy Programming Language (EPL), a Simplified Chinese programming language, demonstrating the attackers‘ sophisticated technical capabilities.
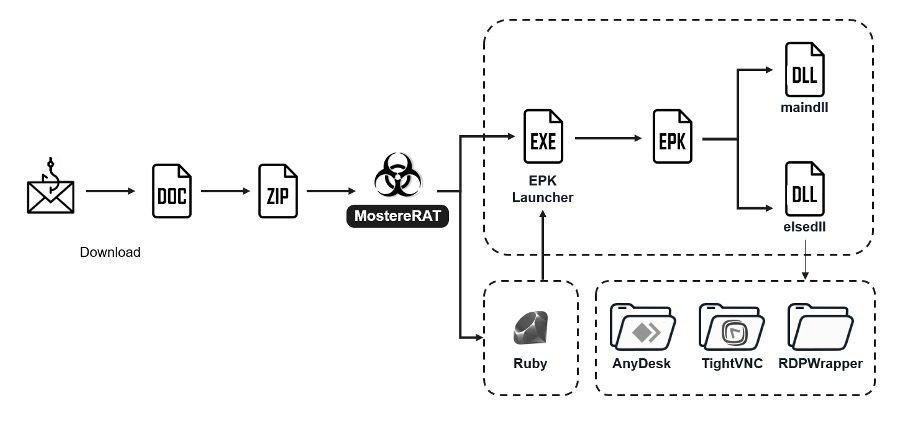
The initial executable, based on wxWidgets menu samples, decrypts bundled tools using a simple SUB operation with key value ‘A’ and places components in C:\ProgramData\Windows.
The malware creates two Windows services – “WpnCoreSvc” for automatic startup execution and “WinSvc_” for demand-start operations – both running with SYSTEM-level privileges through the CreateSvcRpc technique that bypasses standard service creation APIs.
MostereRAT’s EPL-based payload operates through two primary modules. Module 1 (maindll.db) establishes persistence via scheduled tasks and the DnsNetwork service while implementing sophisticated security evasion.
The malware elevates privileges by duplicating the TrustedInstaller token, one of Windows’ most powerful accounts, using code adapted from the NSudo GitHub project.
Security Evasion and Remote Access Tool Integration
The RAT demonstrates advanced anti-detection capabilities by maintaining hardcoded lists of security product paths and names, including 360 Safe, Kingsoft Antivirus, Tencent PC Manager, Windows Defender, ESET, Avira, Avast, and others.
When security solutions are detected, MostereRAT blocks their network traffic using Windows Filtering Platform (WFP) filters, preventing telemetry transmission and alert generation – a technique similar to the EDRSilencer red team tool.
Module 2 (elsedll.db) provides comprehensive remote access functionality through 37 different commands, communicating with command-and-control servers via mutual TLS (mTLS) authentication over TCP port 8000.
The malware deploys legitimate remote monitoring tools, including AnyDesk, TightVNC, and RDP Wrapper, to establish covert access channels that appear as authorized administrative activity.
The RAT supports multiple payload deployment methods, including shellcode injection, DLL execution via rundll32, and EPK file execution.
It creates hidden administrator accounts and modifies registry entries to prevent user visibility while maintaining persistent access. The malware also captures screenshots, logs keystrokes, and monitors specific applications like Qianniu – Alibaba’s Seller Tool.
FortiGuard’s analysis reveals MostereRAT’s communication protocol uses a magic number 1234567890 followed by packet length and command identifiers.
Fortinet protections detect the malware variants as W32/Agent.MTR!tr, W32/Agent.. 295C!tr, and W32/Agent.. 9C1D!tr across FortiGate, FortiMail, FortiClient, and FortiEDR platforms, while FortiGuard CDR services neutralize malicious document macros.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates