A newly tracked phishing campaign, dubbed “Scanception” by Cyble Research & Intelligence Labs (CRIL), is exploiting PDF attachments with embedded QR codes to orchestrate a sophisticated credential-harvesting operation that is largely evading traditional security controls.
This campaign, active across more than 50 nations and targeting critical sectors such as technology, healthcare, manufacturing, and finance, demonstrates a marked shift in phishing tradecraft concentrating attacks on personal mobile devices that typically escape enterprise visibility and defense.
Campaign Moves Beyond Perimeter Security
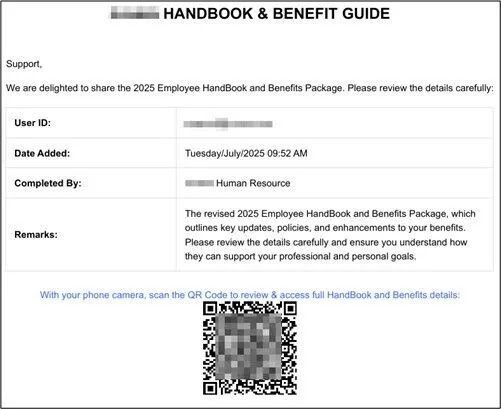
The attack sequence starts with unsuspecting users receiving carefully crafted phishing emails that contain PDF attachments styled to mimic legitimate company documentation, such as HR handbooks or workflow-related notices.

Upon opening the PDF most of which display the organization’s actual logo and proprietary formatting to instill trust victims are prompted, often on the final page, to scan a QR code for further information.
This QR-based lure enables attackers to bypass endpoint protection and secure email gateways, as the ultimate execution happens on personal smartphones, pulling the victim outside the protective bounds of traditional IT monitoring.
Analysis by CRIL has uncovered more than 600 unique phishing PDFs in just three months, with nearly 80% of these files exhibiting zero detections on scanning engines like VirusTotal.
The evolution of these lures, from single-page decoys to multi-page professional-looking documents, reflects adaptive efforts to defeat security solutions that examine only the opening sequence of files.
Once the QR code is scanned, victims are funneled to adversary-controlled infrastructure through a web of abused trusted platforms such as Google, YouTube, Bing, Cisco, and Medium which further conceals the attack’s intent by hiding it behind reputable domains and open redirectors frequently whitelisted by organizations.
Bypassing MFA and Leveraging Open Redirects
Key to the campaign’s effectiveness is its use of sophisticated adversary-in-the-middle (AITM) attack techniques.
After redirect, the phishing site impersonates official login portals such as Microsoft 365’s Office 365 interface.
Custom code actively detects automated analysis tools and debugging attempts, immediately rerouting analysts to benign pages if detected, thus limiting the success of manual forensic investigation.
The phishing page implements a multi-stage credential harvesting process: initial email and password submissions are exfiltrated through randomized backend channels, with real-time communication orchestrated by functions such as sendAndReceive and route generation handled by libraries like randexp.js.
If the victim’s organizational account is protected by multi-factor authentication (MFA), the phishing infrastructure dynamically prompts for additional verification codes, including time-sensitive 2FA tokens or one-time passcodes sent via SMS or email.
This layered AITM approach allows attackers to intercept and relay authentication data to legitimate login portals in real-time, resulting in session hijacking and full account takeover, even where MFA is enabled.
Beyond credential theft, attackers utilize a complex chain of trusted service redirects often encoding victim identifiers in base64 to obfuscate tracking before ultimately depositing victims on legitimate websites to minimize post-attack suspicion.
CRIL’s analysis highlights the global and sector-specific targeting of this campaign, with attack themes carefully customized to exploit familiar organizational workflows and increase the probability of user engagement.
Scanception’s success highlights a troubling trend in phishing: by targeting the mobile devices of enterprise users and leveraging legitimate public cloud infrastructure and open redirect mechanisms, attackers are eroding the boundaries of trust and security.
The campaign demonstrates that reliance on perimeter defenses and basic user training is no longer sufficient as attackers co-opt both human and technical trust to bypass controls and defeat multifactor authentication at scale.
As this campaign remains ongoing, CRIL emphasizes heightened user vigilance and proactive security review of QR code-based communications as critical steps in defending against this newly evolving threat vector.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get More Instant updates