A critical security vulnerability known as Password Reset Poisoning has been discovered that allows attackers to hijack user accounts by manipulating password reset links through Host Header Injection.
This sophisticated attack technique exploits a fundamental vulnerability in how web applications generate password reset URLs, potentially affecting millions of users across various platforms.
Bug bounty hunter and penetration tester Pratik Dabhi recently disclosed a significant security vulnerability that demonstrates how attackers can completely take over user accounts by exploiting weaknesses in password reset functionality.
The vulnerability, identified on a major web application, showcases how improper handling of HTTP headers can lead to devastating security breaches.
The attack begins when users attempt to reset their forgotten passwords through the standard “Forgot Password” feature found on most websites.
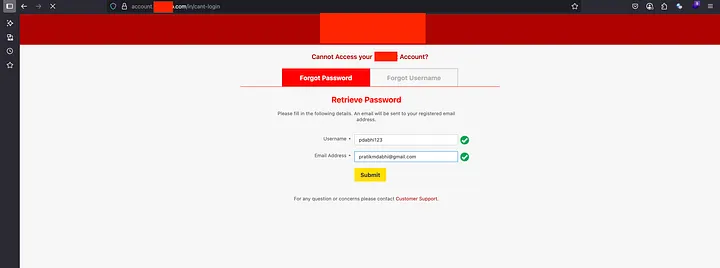
Typically, these systems send users an email containing a unique reset link that allows them to create a new password.
The discovered vulnerability occurs when applications incorrectly rely on user-supplied HTTP headers, specifically the Host header, to construct these reset URLs.
During his reconnaissance phase, Dabhi employed industry-standard tools including Subfinder and Assetfinder for subdomain enumeration, followed by historical URL analysis using Wayback Machine data.
His systematic approach led him to identify the vulnerable endpoint at https://account.example.com/en/cant-login, where the password reset functionality was implemented.
Password Reset Link Vulnerability
The exploitation process involves intercepting the password reset request using tools like Burp Suite and manipulating the Host header to point to an attacker-controlled domain.
When Dabhi modified a legitimate password reset request by changing the Host header from account.example.com to bing.com, the application generated a reset link pointing to the malicious domain instead of the legitimate website.
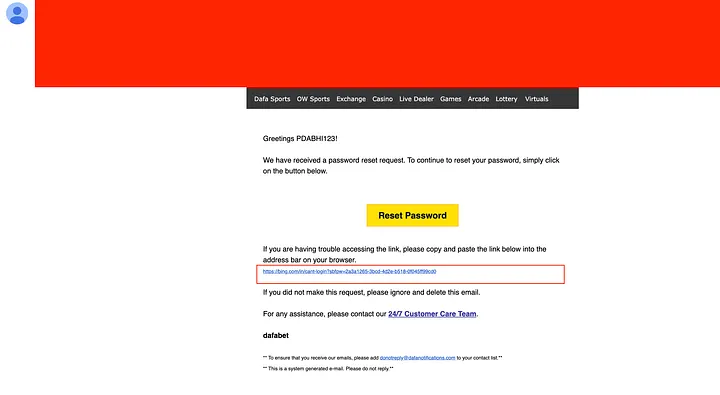
The technical proof-of-concept demonstrated that a standard POST request to /en/cant-login with parameters [email protected]&action=forgot_password could be manipulated by simply altering the Host header.
This manipulation caused the server to generate a password reset link in the format https://bing.com/reset?token=abcdef123456, effectively redirecting the victim’s reset token to the attacker’s infrastructure.
This vulnerability occurs because many web applications dynamically construct URLs using the Host header from incoming HTTP requests without proper validation.
When attackers can control this header, they can redirect password reset links to domains under their control, intercepting the unique tokens required for password resets.
Security Countermeasures
Security experts recommend several critical mitigation strategies. Applications should never rely on user-supplied Host headers when generating password reset links.
The implications of this vulnerability are severe and far-reaching. Successful exploitation allows attackers to completely compromise user accounts, change passwords, and lock legitimate users out of their own accounts.
nce access is gained, attackers can access sensitive personal information, financial data, and confidential business documents stored within compromised accounts.
Beyond immediate data breaches, organizations face significant reputational damage and loss of customer trust when such vulnerabilities are exploited.
The attack’s sophisticated nature makes it particularly dangerous, as victims may not immediately realize their accounts have been compromised.
Instead, they should use server-side configurations like SERVER_NAME to ensure consistent, trusted domain usage.
When Host header functionality is absolutely necessary, applications must validate headers against predefined whitelists of approved domains.
Regular security assessments, including comprehensive penetration testing and code reviews, are essential for identifying and addressing similar vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates.