The Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) has uncovered a new wave of malicious activity where artificial intelligence (AI) is directly integrated into malware operations.
The most prominent discovery, a dropper called PROMPTFLUX, showcases the first known use of “just-in-time” AI a mechanism that enables malware to modify its own code during execution dynamically.
Unlike traditional obfuscation methods, PROMPTFLUX interacts with the Gemini API to rewrite and regenerate its VBScript source code, allowing it to evade signature-based detection by constantly altering structure and content.
Researchers found that PROMPTFLUX leverages Gemini’s “gemini-1.5-flash-latest” model to fetch updated obfuscation logic and executables.
The malware communicates via hard‑coded API keys, issuing specific prompts to Gemini requesting new VBScript variants purely focused on antivirus evasion.
Its module, known as “Thinking Robot,” further automates this cycle by periodically polling the API and saving new regenerated files into the Windows Startup folder to maintain persistence. This approach signals a major advancement toward autonomous, adaptive malware ecosystems powered by LLMs.
Dynamic Regeneration and Early Testing Phases
GTIG’s reverse-engineering analysis identified multiple experimental builds of PROMPTFLUX, including one using a renamed “Thinging” function that instructs Gemini to fully rewrite the malware’s source code every hour.
Each variant embeds the original payload, regeneration logic, and persistent API key, forming a recursive mutation chain.
Although some elements, such as the self‑update function “AttemptToUpdateSelf,” remain commented out, logs written to “% TEMP%\thinking_robot_log.txt.txt” show active communication with Gemini and attempts to process live responses.
At this stage, PROMPTFLUX appears to be under active development rather than wide deployment. Google has since disabled the assets associated with the campaign, noting its early-stage nature.
However, the use of LLMs for runtime metamorphism highlights a potential paradigm shift where malware becomes semi‑autonomous and capable of continual evolution without human reprogramming.
Broader AI Abuse Across Nation-State Operations
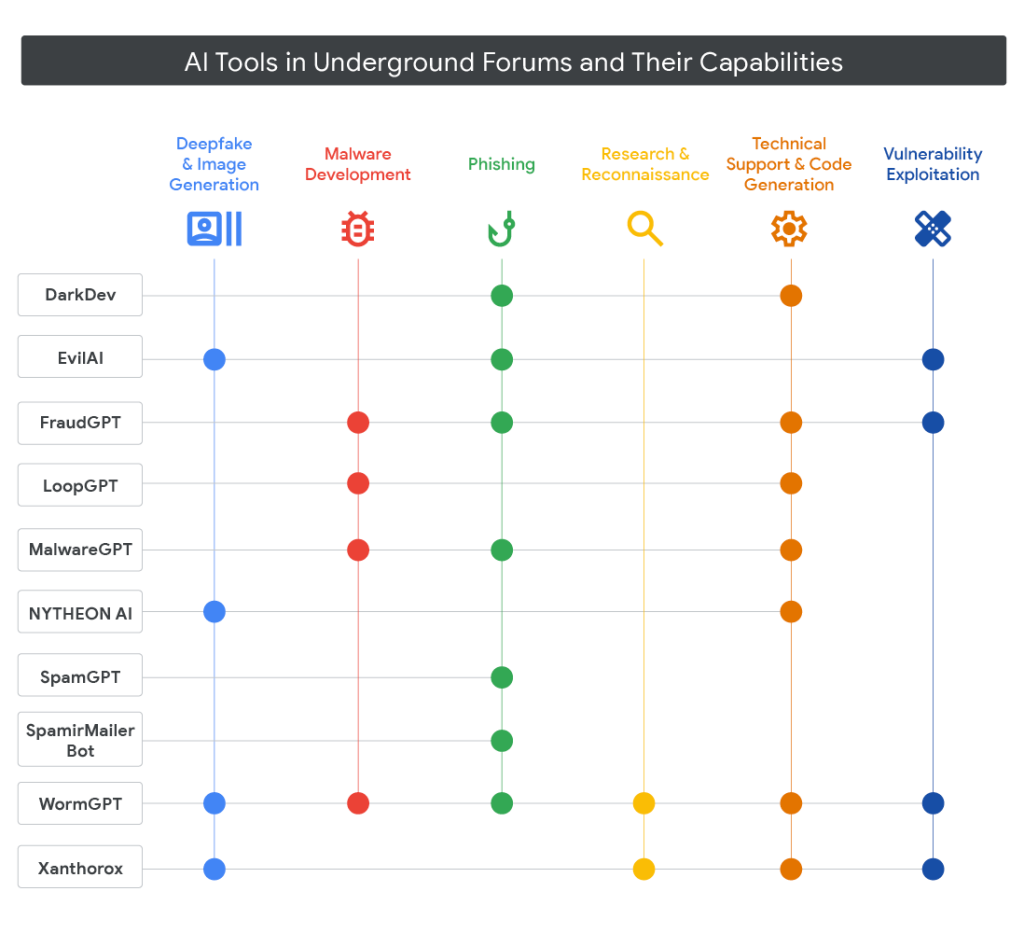
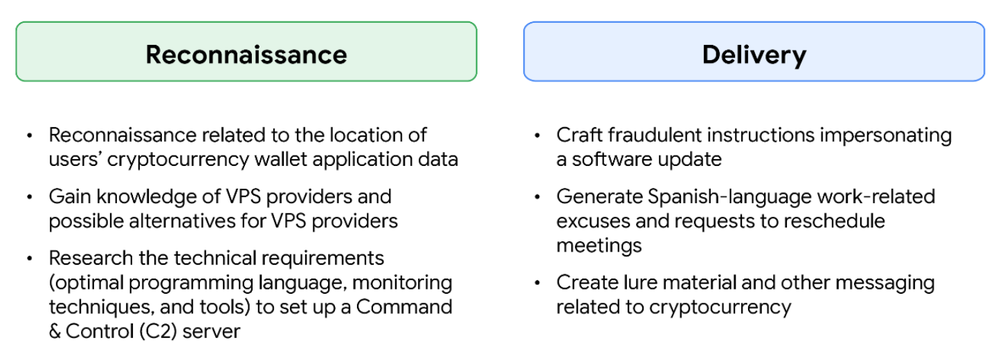
The GTIG report also correlates similar activity with other AI-enabled malware such as PROMPTSTEAL and PROMPTLOCK, uncovering efforts by government-backed and financially motivated actors from North Korea, Iran, and China.
These adversaries are exploiting generative AI systems for phishing content creation, reconnaissance, code generation, and even direct command execution through APIs like Hugging Face and Gemini.
Google has strengthened its defensive classifiers and model safeguards to block such misuse in Gemini.
The company reaffirmed its commitment to responsible AI development through active asset takedowns and enhanced model hardening, ensuring future AI-based malware like PROMPTFLUX will face heightened resistance across the ecosystem.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates