Qilin ransomware, which has rapidly ascended to become the world’s most prevalent ransomware threat in 2025.
Originally developed under the codename “Agent” in 2022 and later recoded in Rust programming language, this sophisticated malware operation has amassed over $50 million in ransom payments in 2024 alone, establishing itself as a dominant force in the global cybercriminal ecosystem.
Qilin, named after the mythical Chinese unicorn symbolizing power and prosperity, represents a new generation of technically advanced ransomware operations.
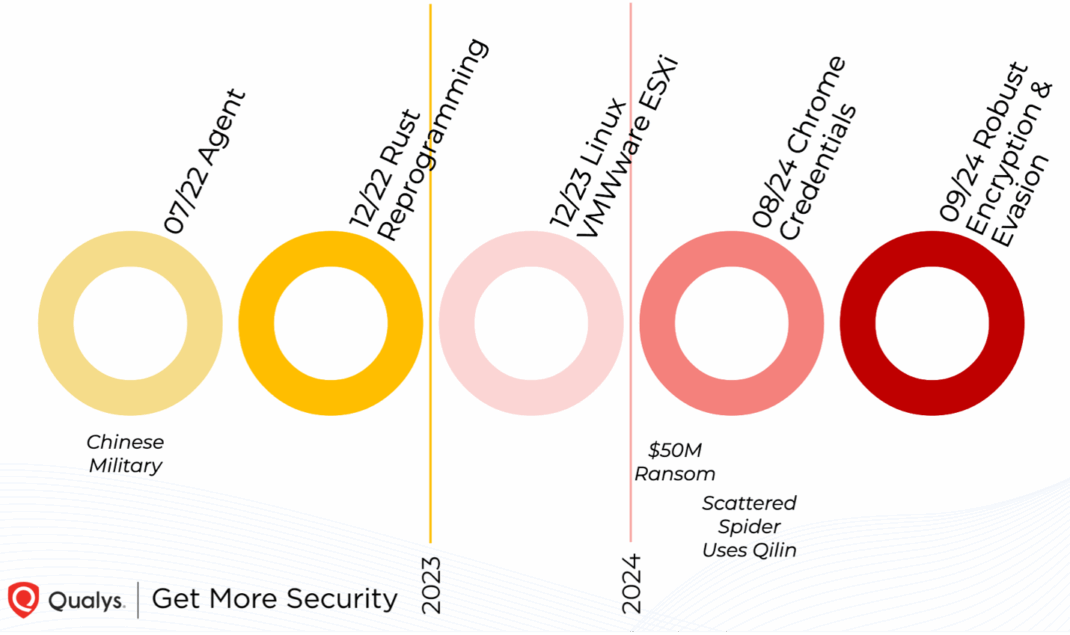
The malware was originally authored by the Dark Web entity “BianLian,” with early deployments linked to clients associated with Chinese military and government-aligned entities according to open-source intelligence.
However, its use has expanded significantly, with notable threat actor groups including Scattered Spiders and entities linked to North Korea now leveraging Qilin in active campaigns.
The ransomware’s recent B variants feature substantial capability upgrades that make it particularly dangerous.
These include Chrome Extension Stealer functionality, enhanced encryption using AES-256-CTR with Optimal Asymmetric Encryption Padding (OAEP), and ChaCha20 for secure communications.
The malware also incorporates AES-NI capabilities for x86 architecture to accelerate encryption processing, making its attacks faster and more difficult to counter.
Qilin’s sophisticated evasion techniques include clearing Windows event logs, deleting itself to hinder forensic analysis, and corrupting backup systems by targeting Windows Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS).
These capabilities force victims into payment scenarios by eliminating recovery options.
Qilin Ransomware Targets Vulnerability
The ransomware operation employs a strategic approach to victim selection, primarily targeting three high-value verticals: manufacturing, legal and professional services, and financial services.
Qilin operators utilize an online assessment tool to estimate potential payouts in advance, focusing their efforts on organizations with substantial financial resources.
An FBI report documented over 1,700 ransomware attacks in 2024, with reported earnings totaling $91 million, though actual figures are likely much higher due to underreporting.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services reported Qilin-related losses ranging from $6 million to $40 million per victim, primarily affecting healthcare and government agencies across the Americas.
The operation’s success stems from its double extortion model, combining rapid encryption with data exfiltration.
Recent attacks have resulted in victims losing tens of thousands of files and terabytes of sensitive data, as demonstrated by airport targets suffering losses of 22,428 files and 2TB of data.
Proactive Defense Measures
Cybersecurity professionals emphasize that Qilin’s widespread reach and varied attack methods make it a top-priority threat across both cybercrime and nation-state threat models.
The ransomware gains initial access through spearphishing campaigns, remote monitoring software exploitation, multifactor authentication bombing, and SIM swapping techniques.
Security experts recommend implementing comprehensive defense strategies including user awareness training, incident response readiness exercises, prioritized vulnerability patching, and immutable backup systems.
Organizations are advised to adopt Zero Trust Architecture with network isolation and segmentation to limit potential damage.
The ransomware’s ability to exploit public-facing applications, including CVE-2023-27532, underscores the critical importance of timely patch management for network-facing systems.
As Qilin continues its aggressive expansion across more than 25 countries, cybersecurity teams must prioritize proactive defensive measures over reactive responses to effectively combat this evolving threat.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates.