Threat researchers at Trend Micro have identified a sophisticated evolution in the Water Saci malware campaign, revealing a script-based infection chain that represents a significant tactical shift for Brazilian-focused cybercriminals.
The newly discovered attack methodology, observed since October 2025, abandons traditional .NET-based payloads in favor of fileless execution techniques leveraging Visual Basic Script (VBS) downloaders and PowerShell automation, dramatically enhancing evasion and persistence capabilities.
The SORVEPOTEL backdoor initiates infection through deceptively named ZIP archives distributed via WhatsApp Web, with files labeled as “Orcamento-2025*.zip” masquerading as legitimate business documents.
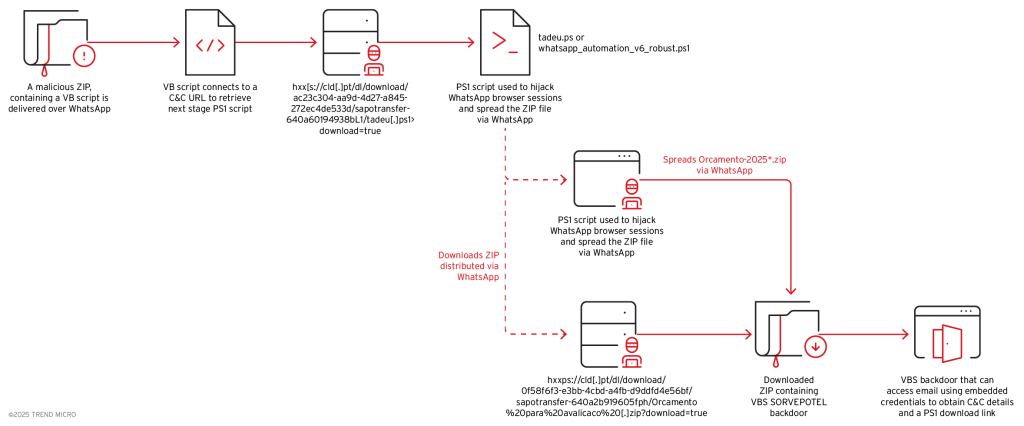
Upon extraction, users encounter Orcamento.vbs, an obfuscated downloader that executes PowerShell commands to deliver fileless tadeu.ps1.
This sophisticated automation script hijacks WhatsApp Web sessions and harvests all contacts from compromised accounts to mass-distribute malicious payloads.
Technical Infrastructure and Multi-Channel Command and Control
The malware implements a dual-channel command-and-control architecture, which distinguishes it from conventional banking trojans.
Rather than relying solely on HTTP-based communication, SORVEPOTEL leverages IMAP connections to hardcoded terra.com.br email accounts, retrieving configuration data and C&C server addresses embedded within email content.
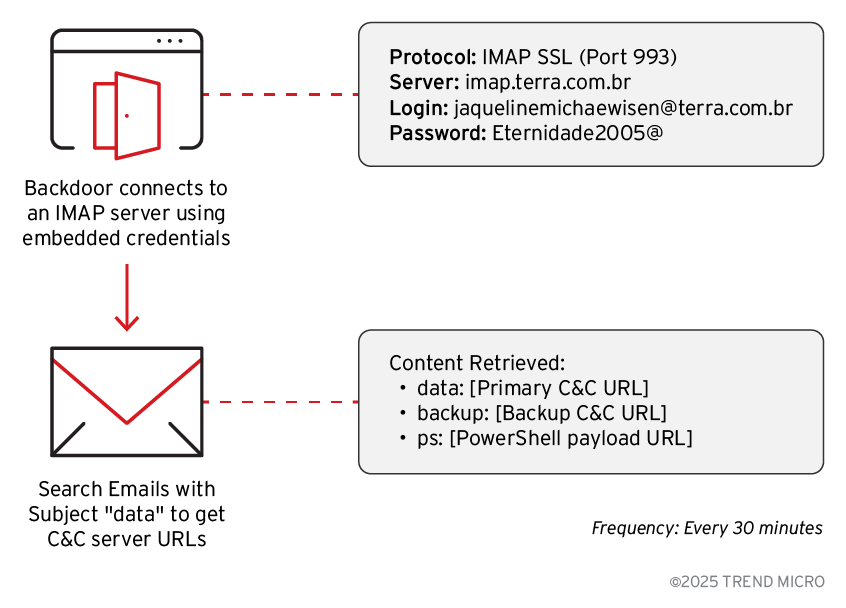
This email-based infrastructure provides operational resilience: if HTTP polling fails, the malware seamlessly transitions to HTTP POST requests to extracted C&C endpoints every 5 seconds, querying for pending commands using the action parameter “get_commands.”
Threat actors have strengthened email account security with multi-factor authentication, though this has introduced operational delays requiring manual entry of authentication codes.
Consequently, researchers observed attackers deploying additional email accounts to streamline campaign execution.
The sophisticated remote control mechanism permits real-time pause and resume capabilities, enabling attackers to coordinate spreading activities across infected machines and respond instantaneously to detection threats through JSON-based control signals.
Advanced Persistence and Evasion Mechanisms
SORVEPOTEL establishes multi-vector persistence through registry modifications and scheduled task creation, deploying a copy of itself, WinManagers.vbs, to C:\ProgramData\WindowsManager\ for survival across system reboots and user sessions.
The malware implements comprehensive anti-analysis capabilities, including language verification restricted to Portuguese-language systems, and debugger detection targeting tools such as OllyDbg, IDA, x32/x64dbg, WinDbg, Process Hacker, and Process Monitor.
It also triggers sophisticated self-destruct mechanisms that create batch files for complete system cleanup upon analysis attempt detection.
Browser profile hijacking represents the malware’s most insidious capability. The malware terminates existing Chrome processes, copies legitimate Chrome profile data, including cookies and authentication tokens, to temporary workspaces, and launches Chrome with specific automation flags while injecting the WA-JS library for WhatsApp control.
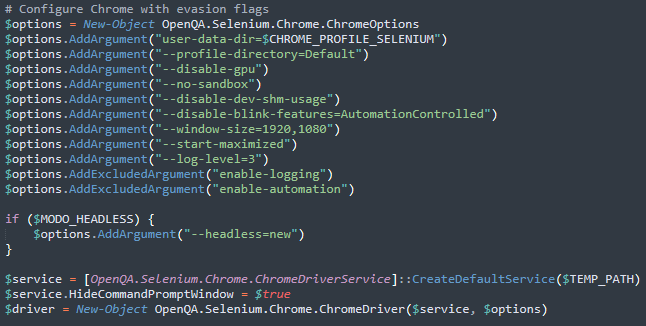
This technique bypasses WhatsApp Web authentication entirely, eliminating the need for QR code scanning and triggering no security alerts.
Campaign statistics demonstrate attackers’ sophisticated measurement capabilities, with detailed telemetry exfiltration enabling precise success rate calculation, victim system profiling, and targeted outreach optimization.
The evolution from compiled banking trojans to script-driven browser automation reflects broader shifts within Brazil’s cybercriminal ecosystem, particularly regarding messaging platform exploitation as a preferred delivery mechanism for scalable, low-artifact attacks against enterprise and consumer targets alike.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates