A new cybercrime toolkit dubbed SpamGPT is transforming the phishing landscape by marrying advanced artificial intelligence with the infrastructure of professional email marketing platforms.
Marketed on underground forums as a “spam-as-a-service” solution, SpamGPT dramatically lowers the technical barrier to entry for criminals seeking to deploy large-scale, highly effective phishing campaigns.
Its polished, dark-themed interface closely resembles legitimate marketing software and offers a suite of capabilities that automate almost every stage of a fraudulent email operation.
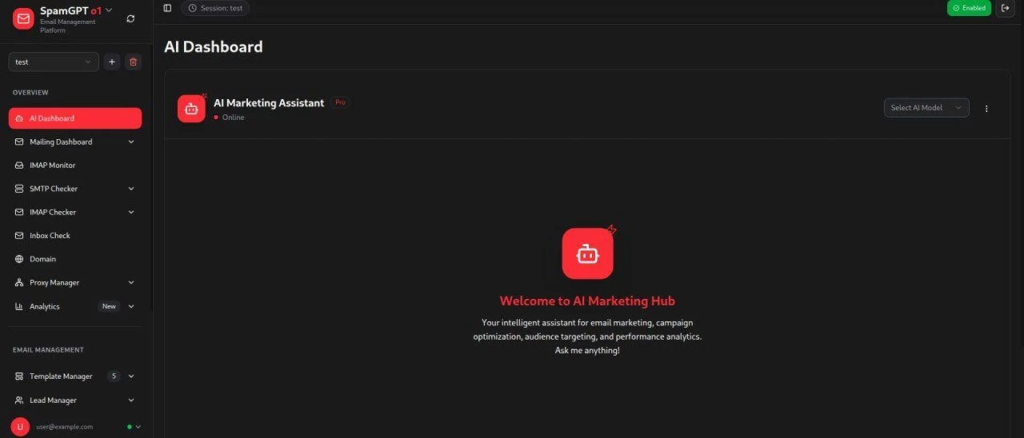
SpamGPT’s creators promote it as an all-in-one platform that blurs the distinction between commercial email marketing tools and weaponized automation.
At its core lies an encrypted, AI-powered framework that includes an integrated assistant branded “KaliGPT,” which attackers can prompt to generate persuasive phishing copy, craft eye-catching subject lines, and tailor content for specific targets.
This eliminates the need for strong writing skills: scammers simply describe their objectives, and the AI produces ready-to-send templates.
Under the guise of a legitimate service, SpamGPT also offers real-time dashboards for agentless monitoring of deliverability and engagement metrics, features usually exclusive to Fortune 500 marketers.
SpamGPT’s Capabilities and Features
Within its comprehensive dashboard, SpamGPT provides modules to configure or compromise SMTP and IMAP servers, test email deliverability, and analyze campaign performance—tasks typically requiring substantial technical expertise.
For a fee of $5,000, customers gain access to an “SMTP cracking mastery” training program, which equips them to create or infiltrate a virtually limitless pool of high-quality SMTP servers.
This turnkey infrastructure empowers even novices to launch massive spam operations while evading detection.
By abusing reputable cloud services such as Amazon AWS and SendGrid, SpamGPT masks malicious traffic to achieve near-guaranteed inbox placement across providers like Gmail, Outlook, and Microsoft 365.
Advanced spoofing techniques are another core selling point. Users can customize email headers and impersonate trusted domains, leveraging valid or forged SMTP credentials to bypass SPF and DKIM checks—particularly effective if the target has not enforced strict DMARC policies.
A bulk-checking utility verifies SMTP and IMAP account credentials in batch, and a built-in inbox placement tester iterates message content until it reliably reaches recipients’ primary inboxes rather than spam folders.
By integrating these powerful features behind a user-friendly graphical interface, SpamGPT converts what was once a high-skill, resource-intensive operation into one manageable by a single operator.
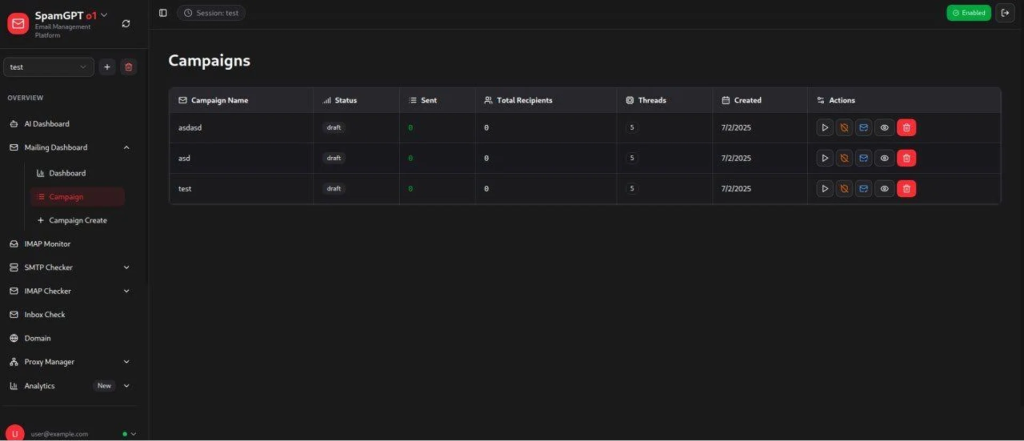
This shift marks a troubling evolution in cybercrime: as automation and intelligent content generation advance, phishing attacks become more scalable, convincing, and challenging to detect.
To counter this threat, organizations must adopt robust email security measures.
Enforcing comprehensive DMARC, SPF, and DKIM policies will raise the bar for domain spoofing.
Simultaneously, deploying AI-driven email security solutions capable of identifying the subtle linguistic patterns and technical fingerprints of AI-generated phishing content is essential.
As attackers harness AI for offense, defenders must leverage equivalent technology and real-time threat intelligence to safeguard their email ecosystems.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates