A security vulnerability has been disclosed affecting Tata Motors, exposing over 70 terabytes of sensitive corporate data, customer information, and infrastructure details through misconfigured AWS credentials and inadequately secured API endpoints.
The breach, discovered in 2023, reveals multiple critical security oversights that allowed unauthorized access to customer databases, financial records, fleet tracking systems, and administrative dashboards.
Exposed AWS Keys Compromise Hundreds of Storage Buckets
The vulnerability originated from AWS access keys exposed in plaintext on E-Dukaan, Tata Motors’ customer-facing e-commerce marketplace for vehicle spare parts.
These credentials granted unrestricted access to multiple S3 buckets containing highly sensitive information, including customer databases, market intelligence reports, hundreds of thousands of invoices with personally identifiable information such as PAN numbers, and approximately 40 gigabytes of administrative order reports.
Remarkably, the exposed keys were utilized to download a single 4-kilobyte file containing tax codes, representing a catastrophic security risk for minimal operational benefit.
The vulnerability extended beyond E-Dukaan to FleetEdge, Tata Motors’ fleet management platform.
A second set of AWS credentials was discovered encrypted client-side within API responses, a security practice that provides no meaningful protection since decryption keys are accessible to attackers.
This second credential set exposed an additional bucket containing 70+ terabytes of fleet data spanning back to 1996, along with write access to production websites.
S3 Browser crashed while estimating the full scope of exposed data in a single bucket, underscoring the massive scale of the exposure.
Hardcoded credentials discovered within E-Dukaan’s source code revealed a critical vulnerability in the organization’s Tableau deployment.
The authentication mechanism relied on a server-side “trusted token” that required only a username and site name, bypassing password verification entirely.
Security researchers were able to obtain valid authentication tokens and gain administrative access to Tableau, providing complete visibility into internal projects, financial reports, and dealer dashboards.
By identifying server administrator credentials through dashboard metadata, attackers could escalate privileges to full administrative control of the analytics platform.
An API key for Azuga, a third-party fleet management platform used by Tata Motors for test drive vehicle tracking, was discovered exposed in JavaScript code.
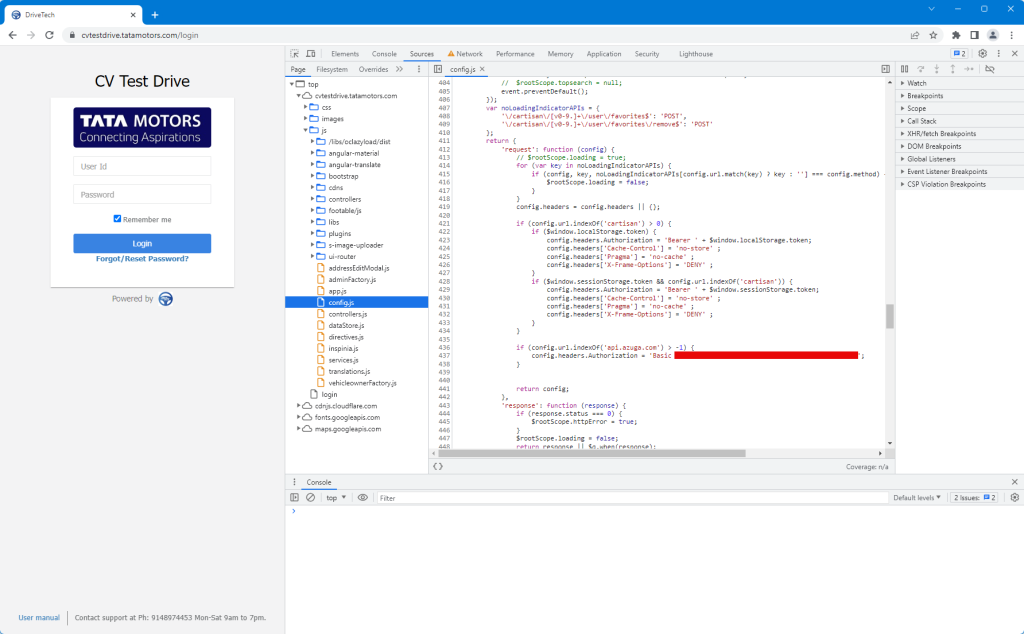
Verification confirmed the token remained valid and functional, granting unauthorized access to the company’s test drive fleet management system and associated vehicle location data.
All exposed credentials have been rotated and are no longer valid. The researcher confirmed that no substantial data exfiltration occurred, and no evidence of malicious third-party access was identified.
The findings underscore critical infrastructure security gaps, including client-side credential encryption, hardcoded authentication tokens, and unnecessarily broad AWS permission scopes.
Organizations should implement comprehensive secrets management, enforce server-side authentication, and adopt principle-of-least-privilege access controls across cloud infrastructure.
Cyber Awareness Month Offer: Upskill With 100+ Premium Cybersecurity Courses From EHA's Diamond Membership: Join Today