The inadvertent installation of a commercial endpoint detection and response (EDR) agent by a threat actor provided an unprecedented inside look at their operational methods.
Huntress analysts leveraged detailed telemetry and browser artifacts to map the adversary’s day-to-day activities, revealing how AI-driven automation, phishing frameworks, and proxy services were woven into their attack lifecycle.
AI-Powered Workflow Automation
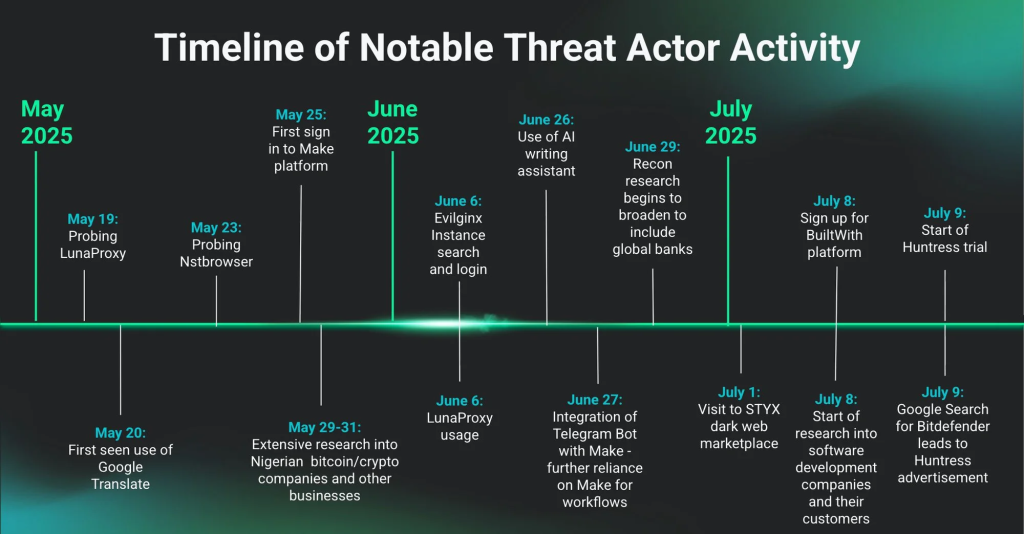
On May 25, the actor signed up for Make.com and began exploring its Telegram Bot integration, using webhooks to initiate automated reconnaissance processes.
EDR telemetry captured process trees for “python.exe” and “node.exe” executing webhook listeners, alongside Chrome history entries searching for “free ai no signup” and “csv generator ai.”
By June 29, the actor’s Make.com workflows, which automated target identification triggered by Telegram tips, were followed by Google Translate-assisted message crafting.
These telemetry signals included outbound API calls to make.com and synchronous HTTP POST requests to Telegram endpoints, illustrating how adversaries embed AI toolchains into their malware-less operations.
Reconnaissance and Phishing Framework Trials
Concurrent with AI workflows, the actor used Censys to discover live instances of the Evilginx man-in-the-middle framework. EDR logs recorded DNS queries to “censys.io” and HTTP GET requests to port-specific endpoints, followed by attempts to connect via “curl.exe.”
Local executions of GraphSpy and Bloodhound were detected, as were sessions of the TeamFiltration framework for network enumeration. Huntress SOC correlated these artifacts with unique machine names previously linked to prior incidents, confirming the adversarial nature of the host.
The actor’s browser history also reflects deep dives into residential proxy services LunaProxy and Nstbrowser, evidenced by the execution of “LunaProxyDivert.exe” and SOCKS5 tunnel configurations captured in EDR process logs.
Across three months and 2,471 unique identity accesses, EDR-driven hunts revealed 20 additional compromised identities through session token theft and malicious mail rule creation.
High-confidence detections against the actor’s Autonomous System infrastructure were developed using aggregated telemetry, significantly reducing investigation time for follow-on incidents.
Although the actor eventually uninstalled the agent, likely upon sensing the data collection, Huntress retained enough artifacts to chart the full attack lifecycle, from initial ad click to sophisticated phishing framework experimentation.
This case underscores the transformative value of EDR telemetry for real-time threat hunting, incident response, and improving community defenses.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates