A sophisticated phishing campaign has emerged, successfully bypassing Secure Email Gateways (SEGs) and evading perimeter defenses by leveraging an advanced phishing script that utilizes random domain selection, dual UUID generation, and dynamic server-driven page replacement.
First spotted by Cofense Intelligence in February 2025, the ongoing campaign exemplifies the rapid evolution of credential theft tactics that prioritize deception and detection evasion.
Phishing Campaign Exploits Unique UUIDs to Evade Secure Email Gateways
Unusually, the phishing script maintains a hardcoded list of 9 randomly generated .org domains devoid of meaningful words an intentional obfuscation technique aimed at circumventing standard blocklists and AI-driven domain analysis tools.
Upon execution, the script uses Math.random() to select only one domain, eliminating traditional failover and redundancy logic commonly found in legacy phishing kits.
This absence of retries both minimizes traffic and reduces the likelihood of detection, making it highly resilient against intrusion detection systems and rate-limiting mechanisms.
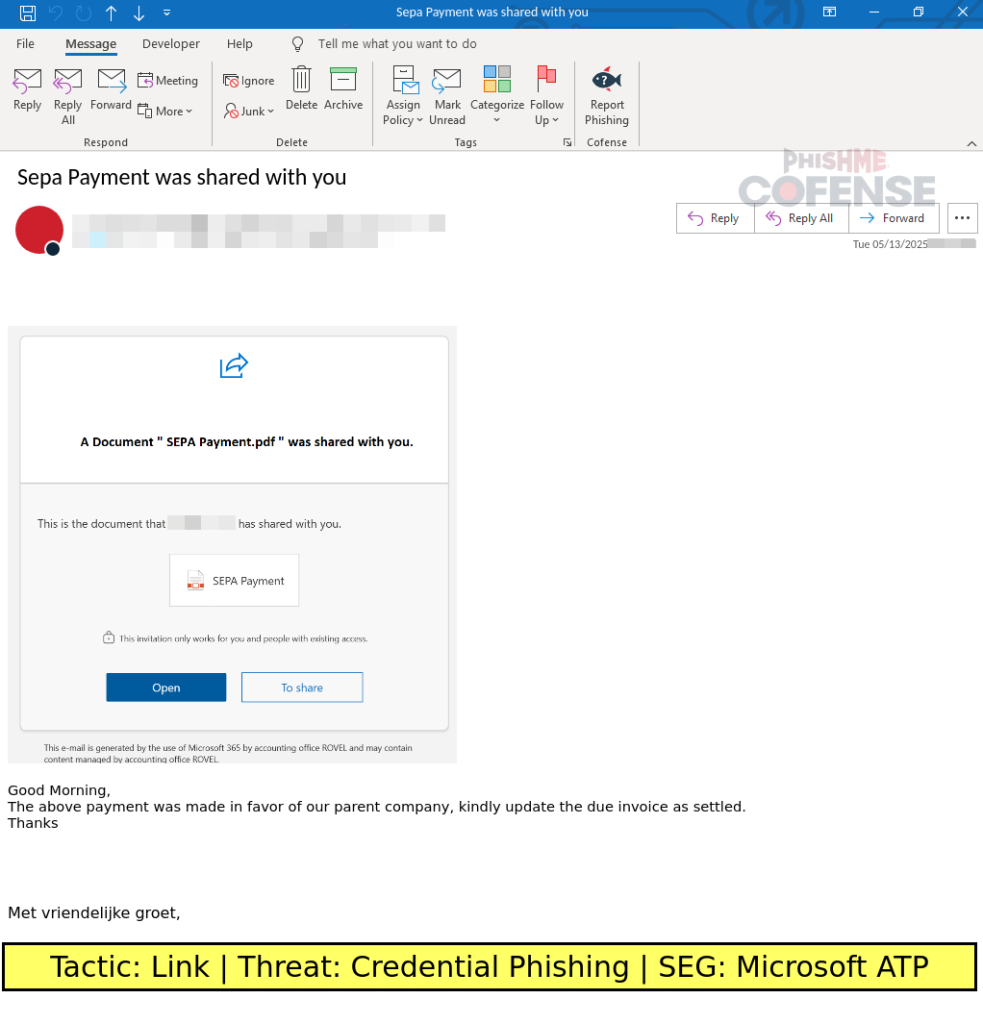
The script also incorporates a dual UUID approach to tracking: a hardcoded campaign UUID and a dynamically generated session-specific UUID using uuidv4() in JavaScript.
The campaign-level UUID enables broad campaign monitoring or targeting specific enterprises. At the same time, the session-level identifier enables granular victim tracking, an advanced tactic reminiscent of legitimate API identifiers used in modern web applications.
Combining these approaches, threat actors can correlate and analyze credential theft on both macro and individual levels, dramatically improving precision and operational control.
Advanced Tactics: HTML Attachments and Dynamic Page Replacement
Delivery typically relies on HTML-based attachments or embedded links that appear to be invitations to access popular cloud collaboration platforms such as Microsoft OneDrive, SharePoint Online, DocuSign, and Adobe Acrobat Sign.
The embedded JavaScript starts by loading jQuery from a reputable CDN, then defines functions for Base64 email decoding, address validation, and UUID generation.
Once an email is validated, the script sends an HTTPS POST request to the randomly chosen .org domain, containing JSON data with the campaign UUID, session UUID, server, and plaintext email address.
Crucially, instead of redirecting users to a new site, the script performs dynamic page replacement—refreshing the page’s content with a server-generated, fake login form featuring corporate branding that matches the victim’s employer.
This technique, which aligns with MITRE ATT&CK T1185 (Browser Session Hijacking), enables seamless, real-time deception without revealing the attacker’s infrastructure.
Attributing trust to .org domains and minimizing suspicious network activity, these campaigns maximize user trust while evading conventional web filtering and detection tools.
As phishing actors adopt increasingly sophisticated infrastructure and scripting, defenders must stay vigilant, adapting threat intelligence, detection strategies, and user awareness programs to address these nuanced, high-speed credential harvesting attacks.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News , LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates