Cloudflare, a leading internet security and infrastructure provider, has accused Perplexity AI, an emerging AI-powered answer engine, of circumventing web protections to crawl content from millions of websites, despite explicit blocks.
According to a detailed technical report published by Cloudflare, Perplexity’s crawling behavior includes user-agent manipulation, evading robots.txt directives, and rotating IP addresses and Autonomous Systems (ASNs) to skirt network restrictions.
AI Crawler Found Using Stealth Tactics
Cloudflare’s investigation was prompted by customer complaints, including reports that Perplexity was accessing restricted content even after its bots PerplexityBot and Perplexity-User were explicitly blocked using both robots.txt files and Web Application Firewall (WAF) rules.
In tightly controlled tests, Cloudflare created new, non-indexed domains with restrictive crawling policies and attempted to access content via Perplexity.
Surprisingly, the platform was able to retrieve and summarize protected content from these domains, which had no public discoverability and forbade all bot access.
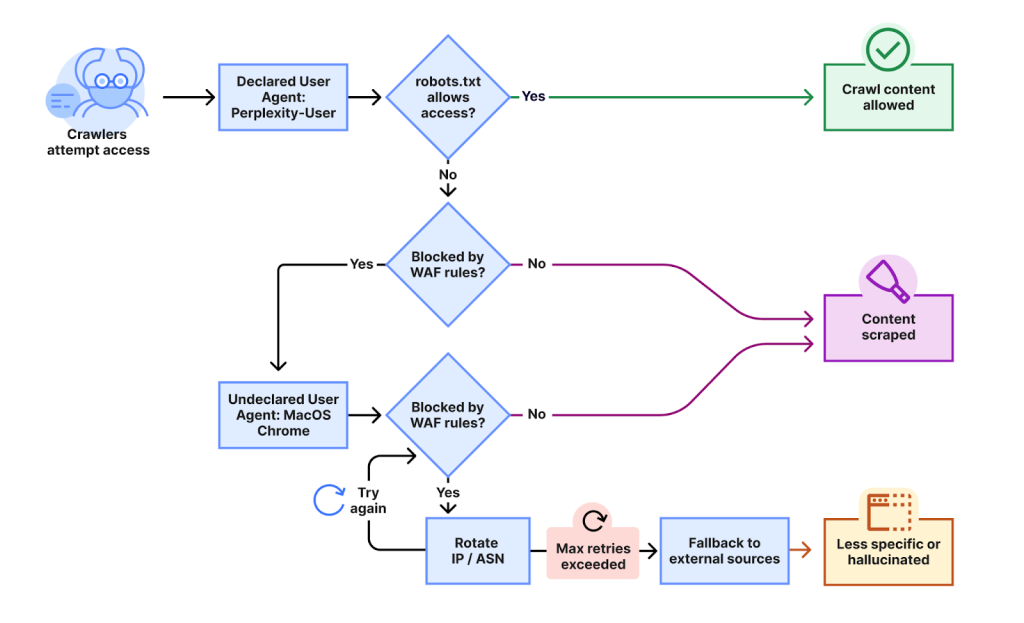
Technical analysis revealed that Perplexity’s crawling infrastructure initially used its declared user-agents, which identify themselves as bots.
When these were blocked, however, the company allegedly deployed crawlers impersonating generic browsers such as Chrome on macOS, using user-agent strings like:
textMozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/124.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
Cloudflare observed 3–6 million daily requests from these stealth agents, alongside the 20–25 million daily requests from Perplexity’s declared bots.
In addition to user-agent obfuscation, Perplexity reportedly rotated through multiple IP addresses and ASNs not officially linked to their public documentation. This IP churn made it challenging for standard block lists or firewall rules to keep pace, effectively bypassing standard anti-bot protections.
Industry Standards and Content Protection
Cloudflare contrasted Perplexity’s tactics with those of other AI companies, such as OpenAI, which are said to follow internet norms: using unique and declared user-agents, fetching and respecting robots.txt rules, and halting all attempts to crawl when disallowed.
Cloudflare’s experiment with OpenAI’s ChatGPT showed full compliance with these expectations, while Perplexity continued to probe blocked sites via alternate means.
To mitigate such stealth activity, Cloudflare has upgraded its managed rules to fingerprint and block Perplexity’s obfuscated crawlers, providing these protections even to free-tier customers. Over 2.5 million websites now use Cloudflare’s managed robots.txt feature or AI Crawler block rules.
As the web shifts toward more explicit controls over AI-powered scraping and content training, Cloudflare urges increased transparency and technical accountability from bot operators. The company also signals ongoing collaboration with standards groups to enforce responsible data access.
Cloudflare’s findings serve as a warning for AI companies building on internet data: transparency, compliance with robots.txt, and respect for content creator preferences remain non-negotiable terms for a trustworthy and sustainable web.