In a shocking development, another Indonesian government website has fallen victim to cyberattacks, marking an alarming trend in the country’s digital infrastructure vulnerabilities.
The targeted site, associated with the Central Java Provincial Government’s e-office system, was defaced by a hacker identified as “Atengg377,” who left their digital signature on the compromised page.
This incident highlights Indonesia’s ongoing struggle with cybersecurity threats.
Details of the Attack
According to the post from cyberfeeddigest, the defacement of the website involved altering its visual appearance and content, replacing legitimate information with unauthorized material.
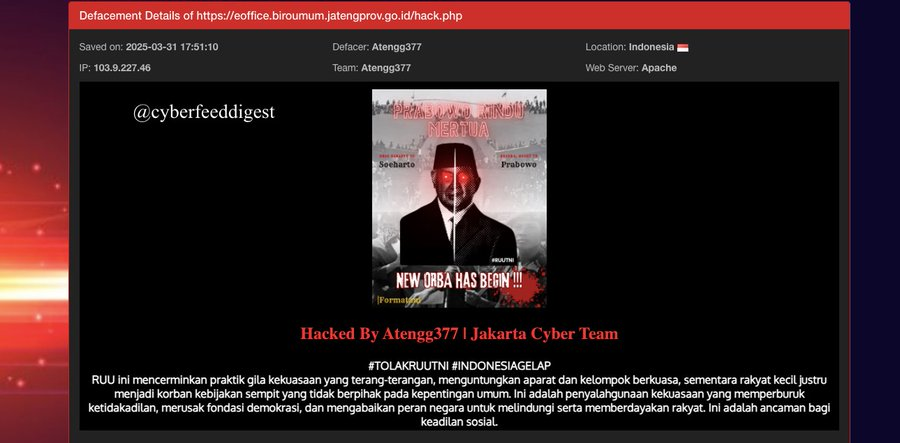
Such attacks are often executed by exploiting vulnerabilities in web servers or content management systems (CMS).
Common techniques include SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and brute-force attacks to gain unauthorized access to administrative privileges.
In this specific case, the hacker used a defacement technique that likely involved modifying the site’s core files or injecting malicious code into its scripts.
For example, a typical payload for defacement could look like this:
document.body.innerHTML="Hacked by Atengg377Your security is weak!";Such scripts allow attackers to overwrite the website’s content dynamically, leaving behind messages or visual elements that showcase their hacking prowess.
Motivations Behind Website Defacements
Website defacements can serve various purposes:
- Hacktivism: Some attackers use defacement as a platform to express political or social grievances. In previous cases involving Indonesian hackers, messages have criticized corruption and governance issues.
- Cyber Vandalism: Others deface websites for notoriety or to mock site owners by exposing security flaws.
- Competitions Among Hackers: Defacers often engage in informal contests to demonstrate technical skills and gain recognition within underground hacking communities.
While no explicit political message was left by Atengg377 in this attack, their actions continue a pattern of targeting high-profile government platforms.
Indonesia’s Cybersecurity Challenges
Indonesia has seen a surge in cyberattacks targeting government websites over recent years.
From ransomware incidents crippling national data centers to widespread defacements of local government sites, these attacks underscore systemic weaknesses in cybersecurity practices.
In December 2024 alone, over 50 websites were defaced across the country.
Key vulnerabilities exploited in such attacks include:
- Unpatched Systems: Outdated software leaves websites open to known exploits.
- Weak Passwords: Brute-force attacks can easily crack predictable login credentials.
- Insecure Web Applications: Poorly configured CMS platforms are prone to SQL injection and XSS vulnerabilities.
Mitigation and Recovery Measures
To address these recurring threats, experts recommend several preventive measures:
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify weak points.
- Software Updates: Ensure all web servers and CMS platforms are updated with the latest security patches.
- Strong Authentication Protocols: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and enforce robust password policies.
- Backup Systems: Maintain secure backups to restore services quickly after an attack.
Impact on Public Trust
Cyberattacks on government websites erode public confidence in digital infrastructure and governance.
The repeated targeting of official platforms highlights the urgent need for Indonesia to strengthen its cybersecurity framework.
Without significant reforms, such incidents will continue to undermine governmental operations and public trust.
As hackers like Atengg377 persist in exploiting vulnerabilities, Indonesia must prioritize investments in advanced cybersecurity technologies and training programs for IT personnel across all levels of government.
This latest attack serves as a stark reminder that robust defenses are essential to safeguard critical digital assets against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Also Read: