LockBit ransomware operators have significantly refined their attack methodology, employing sophisticated techniques like DLL sideloading and masquerading to evade detection and maximize encryption impact.
These methods allow attackers to execute malicious code under the guise of trusted applications, making detection increasingly challenging for traditional security solutions.
DLL Sideloading Exploits System Trust
DLL sideloading represents a particularly insidious attack vector where legitimate applications inadvertently load malicious Dynamic Link Libraries instead of their intended counterparts.
LockBit operators strategically place malicious DLLs with identical names to legitimate ones in directories that applications search first during the loading process.
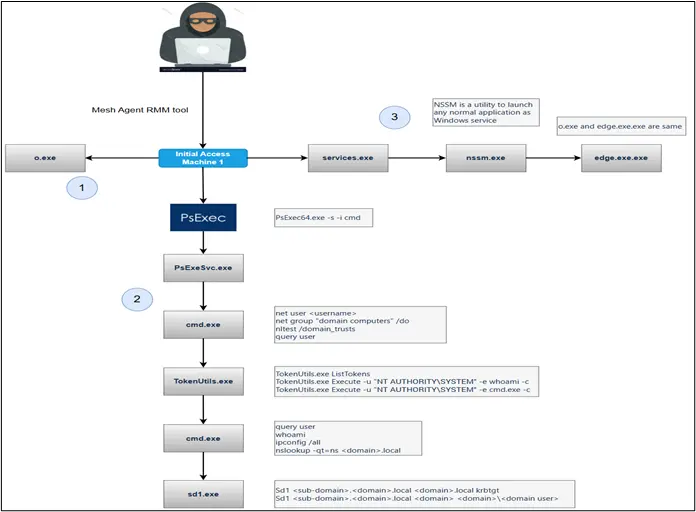
Recent attacks have demonstrated sophisticated implementation of this technique across multiple legitimate applications.
Attackers bundled malicious DLLs with trusted, digitally signed applications, including Jarsigner.exe with jli.dll from the Java platform, MpCmdRun.exe with mpclient.dll from Windows Defender, and Clink_x86.exe with clink_dll_x86.dll from the Clink command-line enhancement tool.
In each case, when the legitimate executable launched, it automatically loaded the corresponding malicious DLL, initiating the ransomware payload execution.
Advanced Masquerading and Attack Chain Integration
Beyond DLL sideloading, LockBit operators employ comprehensive masquerading techniques, renaming malicious executables to mimic standard system files like svchost.exe and explorer.exe.
They leverage legitimate system directories, such as C:\Windows\System32, and utilize authentic application icons to disguise their presence further.
The complete attack chain demonstrates remarkable sophistication, beginning with remote access through tools like MeshAgent and TeamViewer.
Attackers escalate privileges using NSSM (Non-Sucking Service Manager) to run remote access trojans as services and employ PsExec for SYSTEM-level command execution.
Discovery phases utilize standard Windows utilities, including Net.exe, nltest.exe, and query.exe, to enumerate domain structures and user permissions.
Credential theft operations deploy specialized tools like TokenUtils.exe for token manipulation and Sd1.exe for Kerberos ticket extraction.
Lateral movement occurs through Group Policy deployment, distributing ransomware payloads, trusted applications for DLL sideloading, and PowerShell scripts across the network.
Detection and Mitigation Challenges
According to the report, The FBI estimates LockBit’s original operators, led by the now-indicted Dimitry Khoroshev, extorted approximately $500 million since 2019.
Following law enforcement disruption in 2024 and the subsequent leak of LockBit 3.0 builders, these techniques remain accessible to various threat actors.
Security solutions now incorporate multiple detection layers, including file-based signatures (Ransom.LockBit, Heur.AdvML.B!100), behavioral analysis (SONAR.Ransomware variants), and adaptive protections targeting specific techniques like PSEXEC launches and LSASS access patterns.
Network monitoring focuses on identifying remote access tool communications and command-and-control traffic categorized under malicious sources.
Organizations must implement comprehensive endpoint detection capabilities and maintain vigilance against these evolving evasion techniques to protect against LockBit and similar ransomware variants.
Indicators of Compromises (IoCs):
| File Indicator Hash | File Name |
|---|---|
| f689ee9af94b00e9e3f0bb072b34caaf207f32dcb4f5782fc9ca351df9a06c97 | Nssm.exe |
| 5ca8e1d001a2c3800afce017424ca471f3cba41f9089791074a9cb7591956430 | Tokenutils.exe |
| 0201a6dbe62d35b81d7cd7d7a731612458644b5e3b1abe414b0ea86d3266ab03 | sd1.exe |
| 1cd644b750884906b707419c8f40598c04f1402e4e93cbf4a33f3254846dc870 | .exe (Masqueraded MpCmdRun.exe) |
| edcf76600cd11ef7d6a5c319087041abc604e571239fe2dae4bca83688821a3a | mpclient.dll |
| 011b31d7e12a2403507a71deb33335d0e81f626d08ff68575a298edac45df4cb | access.exe (Masqueraded clink_x86.exe) |
| 4147589aa11732438751c2ecf3079fb94fa478a01ac4f08d024fb55f7ffb52f3 | clink_dll_x86.dll |
| 10f1a789e515fdaf9c04e56b8a5330cfb1995825949e6db8c9eaba4ea9914c97 | jarsigner.exe |
| 086567b46fca2a27d404d9b61bdb482394e1591dc13f1302b813bb2ddf5e54cf | jli.dll |
| 6285d32a9491a0084da85a384a11e15e203badf67b1deed54155f02b7338b108 | nxc.exe |
| 785e5aaecd9430451f4b0bad637658e6afeea1e722b3d0dd674cb6a11f4ce286 | encth.exe, dwa.exe |
| 24480dbe306597da1ba393b6e30d542673066f98826cc07ac4b9033137f37dbf | o.exe, edge.exe.exe |
| Network Indicator |
|---|
| msupdate[.]updatemicfosoft[.]com |
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates